Q.No:1 CSIR Dec-2014
Consider the crystal structure of sodium chloride which is modeled as a set of touching spheres. Each sodium atom has a radius \(r_1\) and each chlorine atom has a radius \(r_2\). The centres of the spheres form a simple cubic lattice. The packing fraction of this system is
(1)
\(\pi\left[\left(\frac{r_1}{r_1+r_2}\right)^3+\left(\frac{r_2}{r_1+r_2}\right)^3\right]\)
(2)
\(\frac{2\pi}{3} \frac{r_1^3+r_2^3}{(r_1+r_2)^3}\)
(3)
\(\frac{r_1^3+r_2^3}{(r_1+r_2)^3}\)
(4)
\(\pi \frac{r_1^3+r_2^3}{2(r_1+r_2)^3}\)
Check Answer
Option 2
Q.No:2 CSIR June-2015
X-ray of wavelength \(\lambda = a\) is reflected from the (111) plane of a simple cubic lattice. If the lattice constant is \(a\), the
corresponding Bragg angle (in radian) is
(1)
\(\pi/6\)
(2)
\(\pi/4\)
(3)
\(\pi/3\)
(4)
\(\pi/8\)
Check Answer
Option 3
Q.No:3 CSIR Dec-2015
The first order diffraction peak of a crystalline solid occurs at a scattering angle of \(30^{\circ}\) when the diffraction pattern is recorded using an x-ray beam of wavelength \(0.15 \text{ nm}\). If the error in measurements of the wavelength and the angle are \(0.01 \text{ nm}\) and \(1^{\circ}\) respectively, then the error in calculating the interplanar spacing will approximately be
(1)
\(1.1\times 10^{-2} \text{ nm}\)
(2)
\(1.3\times 10^{-4} \text{ nm}\)
(3)
\(2.5\times 10^{-2} \text{ nm}\)
(4)
\(2.0\times 10^{-3} \text{ nm}\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:4 CSIR Dec-2016
Consider a hexagonal lattice with basis vectors as shown in the figure below.
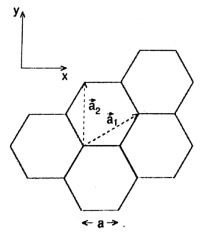
If the lattice spacing is \(a=1\), the reciprocal lattice vectors are
(1)
\(\left(\frac{4\pi}{3}, 0\right), \left(-\frac{2\pi}{3}, \frac{2\pi}{\sqrt{3}}\right)\)
(2)
\(\left(\frac{4\pi}{3}, 0\right), \left(\frac{2\pi}{3}, \frac{2\pi}{\sqrt{3}}\right)\)
(3)
\(\left(0, \frac{4\pi}{\sqrt{3}}\right), \left(\pi, \frac{2\pi}{\sqrt{3}}\right)\)
(4)
\(\left(\frac{2\pi}{3}, \frac{2\pi}{\sqrt{3}}\right), \left(-2\pi, \frac{2\pi}{\sqrt{3}}\right)\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:5 CSIR June-2018
Sodium Chloride \({NaCl}\) crystal is a face-centred cubic lattice, with a basis consisting of \({Na^{+}}\) and \({Cl^{-}}\) ions separated by half the body diagonal of a unit cube. Which of the planes corresponding to the Miller indices given below will not give rise to Bragg reflection of X-rays?
(1)
\(\begin{pmatrix}2&2&0\end{pmatrix}\)
(2)
\(\begin{pmatrix}2&4&2\end{pmatrix}\)
(3)
\(\begin{pmatrix}2&2&1\end{pmatrix}\)
(4)
\(\begin{pmatrix}3&1&1\end{pmatrix}\)
Check Answer
Option 3
Q.No:6 CSIR June-2018
Hard discs of radius \(R\) are arranged in a two-dimensional triangular lattice. What is the fractional area occupied by the discs in the closest possible packing?
(1)
\(\frac{\pi \sqrt{3}}{6}\)
(2)
\(\frac{\pi}{3\sqrt{2}}\)
(3)
\(\frac{\pi \sqrt{2}}{5}\)
(4)
\(\frac{2\pi}{7}\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:7 CSIR June-2019
The third-nearest neighbour distance in a BCC (Body Centered Cubic) crystal with lattice constant \(a_0\) is
(1)
\(a_0\)
(2)
\(3a_0/2\)
(3)
\(\sqrt{3}a_0\)
(4)
\(\sqrt{2}a_0\)
Check Answer
Option 4
Q.No:8 CSIR Assam Dec-2016
The basis vectors of a two-dimensional Bravais lattice are \(\vec{e}_1=\frac{1}{2}\hat{i}+\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\hat{j}\) and \(\vec{e}_2=\frac{1}{2}\hat{i}-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\hat{j}\). A choice of basis vectors for the reciprocal lattice can be
(1)
\(\frac{4\pi}{\sqrt{3}}\left(\frac{1}{2}\hat{i}-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\hat{j}\right)\) and \(\frac{4\pi}{\sqrt{3}}\left(\frac{1}{2}\hat{i}+\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\hat{j}\right)\)
(2)
\(\frac{4\pi}{\sqrt{3}}\left(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\hat{i}+\frac{1}{2}\hat{j}\right)\) and \(\frac{4\pi}{\sqrt{3}}\left(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\hat{i}-\frac{1}{2}\hat{j}\right)\)
(3)
\(2\pi\left(\frac{1}{2}\hat{i}+\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\hat{j}\right)\) and \(2\pi\left(\frac{1}{2}\hat{i}-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\hat{j}\right)\)
(4)
\(2\pi\left(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\hat{i}+\frac{1}{2}\hat{j}\right)\) and \(2\pi\left(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\hat{i}-\frac{1}{2}\hat{j}\right)\)
Check Answer
Option 2
Q.No:9 CSIR June-2020
A lattice is defined by the unit vectors \(\vec{a}_1=a\hat{i}, \vec{a}_2=-\frac{a}{2}\hat{i}+\frac{a\sqrt{3}}{2}\hat{j}\) and \(\vec{a}_3=a\hat{k}\), where \(a>0\) is a constant. The spacing between the (\(100\)) planes of the lattice is
(1)
\(\sqrt{3}a/2\)
(2)
\(a/2\)
(3)
\(a\)
(4)
\(\sqrt{2}a\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:10 CSIR Feb-2022
Potassium chloride forms an \(FCC\) lattice, in which \(K\) and \(Cl\) occupy alternating sites.
The density of \(KCl\) is \(1.98 g/cm^3\) and the atomic weights of \(K\) and \(C\)l are \(39.1\) and \(35.5\) ,
respectively. The angles of incidence (in degrees) for which Bragg peaks will appear when X -
ray of wavelength \(0.4\)nm is shone on a \(KCl\) crystal are
(1)
\(18.5 ,39.4\) and \(72.2\)
(2)
\(19.5\) and \(41.9\)
(3)
\(12.5 ,25.7 , 40.5\) and \(60.0\)
(4)
\(13.5 ,27.8 , 44.5\) and \(69.0\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:11 CSIR Sep-2022
The Figures (i), (ii) and (iii) below represents equilateral triangle, a rectangle and a hexagon respectively.

Which of these can be primitive unit cell of a Bravais lattice in two dimension ?
(1)
only (i) and (iii) but not (ii)
(2)
only (i) and (ii) but not (iii)
(3)
only (ii) and (iii) but not (i)
(4)
all of them
Check Answer
Option 3
Q.No:12 CSIR June-2023
A lattice A consists of all points in three-dimensional space with coordinated (\(n_x,n_y,n_z\)) where \(n_x\), \(n_y\) and \(n_z\) are integers with \(n_x+n_y+n_z\) being odd integers. In another lattice B, \(n_x+n_y+n_z\) are even integers. The lattices A and B are
1) both BCC
2) both FCC
3) BCC and FCC, respectively
4) FCC and BCC, respectively
Check Answer
Option 2
Q.No:13 CSIR Dec-2023
The lattice constant of the bcc structure of sodium metal is \(4.22 A\). Assuming the mass of the electron inside the metal to be the same as free electron mass, the free electron Fermi energy is closest to
1) \(3.2 \hspace{3mm}eV\)
2) \(2.9 \hspace{3mm}eV\)
3) \(3.5 \hspace{3mm}eV\)
4) \(2.5\hspace{3mm} eV\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:14 CSIR Dec-2023
In the section of an infinite lattice shown in the figure below, all sites are occupied by identical hard circular discs so that the resulting structure is tightly packed.
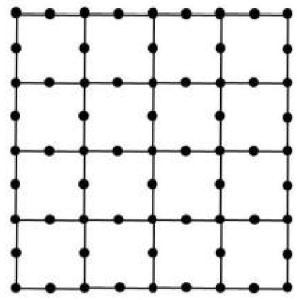
The packing fraction is
1) \( \frac{3\pi}{4} \)
2) \( \frac{\pi}{4} \)
3) \( \frac{3\pi}{16} \)
4) \( \frac{9\pi}{16} \)
Check Answer
Option 3
Q.No:15 CSIR Dec-2024
The lattice spacing in a simple cubic lattice is given to be \(5\,\text{Å}\).
The number of lattice points per square nanometer in the lattice plane
with Miller index \((212)\) is closest to
1) 7.5
2) 3
3) 1.33
4) 0.66
Check Answer
Option 3
Q.No:1 GATE-2012
A simple cubic crystal with lattice parameter \(a_c\) undergoes transition into a tetragonal structure with lattice parameters \(a_t=b_t=\sqrt{2}a_c\) and \(c_t=2a_c\), below a certain temperature. The ratio of the interplanar spacings of \(\begin{pmatrix}1&0&1\end{pmatrix}\) planes for the cubic and the tetragonal structures is
(A)
\(\sqrt{\frac{1}{6}}\)
(B)
\(\frac{1}{6}\)
(C)
\(\sqrt{\frac{3}{8}}\)
(D)
\(\frac{3}{8}\)
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:2 GATE-2013
A lattice has the following primitive vectors (in Angstroms): \(\vec{a}=2(\hat{j}+\hat{k}), \vec{b}=2(\hat{k}+\hat{i}), \vec{c}=2(\hat{i}+\hat{j})\). The reciprocal lattice corresponding to the above lattice is
(A)
BCC lattice with cube edge of \(\left(\frac{\pi}{2}\right)\) Angstrom \({}^{-1}\)
(B)
BCC lattice with cube edge of \(\left(2\pi\right)\) Angstrom \({}^{-1}\)
(C)
FCC lattice with cube edge of \(\left(\frac{\pi}{2}\right)\) Angstrom \({}^{-1}\)
(D)
FCC lattice with cube edge of \(\left(2\pi\right)\) Angstrom \({}^{-1}\)
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:3 GATE-2014
The Miller indices of a plane passing through the three points having coordinates \((0, 0, 1), (1, 0, 0), \left(\frac{1}{2}, \frac{1}{2}, \frac{1}{4}\right)\) are
(A)
\((212)\)
(B)
\((111)\)
(C)
\((121)\)
(D)
\((211)\)
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:4 GATE-2014
Neutrons moving with speed \(10^3 m/s\) are used for the determination of crystal structure. If the Bragg angle for the first order diffraction is \(30^{\circ}\), the interplanar spacing of the crystal is _____________ Angstrom.. (Given: \(m_n=1.75\times 10^{-27} kg, h=6.626\times 10^{-34} J.s\))
Check Answer
Ans 3.91-4.15
Q.No:5 GATE-2015
The lattice parameters \(a, b, c\) of an orthorhombic crystal are related by \(a=2b=3c\). In units of \(a\), the interplanar separation between the \((110)\) planes is _________________ (upto three decimal places)
Check Answer
Ans 0.445-0.450
Q.No:6 GATE-2016
Atoms, which can be assumed to be hard spheres of radius \(R\), are arranged in an \(fcc\) lattice with lattice constant \(a\), such that each atom touches its nearest neighbours. Take the center of one of the atoms as the origin. Another atom of radius \(r\) (assumed to be hard sphere) is to be accommodated at a position \((0, a/2, 0)\) without distorting the lattice. The maximum value of \(r/R\) is __________. (Give your answer upto two decimal places)
Check Answer
Ans 0.40-0.42
Q.No:7 GATE-2017
The total energy of an inert-gas crystal is given by \(E(R)=\frac{0.5}{R^{12}}-\frac{1}{R^6}\) (in eV), where \(R\) is the inter-atomic spacing in Angstroms. The equilibrium separation between the atoms is ___________________ Angstroms. (up to two decimal places).
Check Answer
Ans 0.90-1.10
Q.No:8 GATE-2017
The real space primitive lattice vectors are \(\vec{a}_1=a\hat{x}\) and \(\vec{a}_2=\frac{a}{2}(\hat{x}+\sqrt{3}\hat{y})\). The reciprocal space unit vectors \(\vec{b}_1\) and \(\vec{b}_2\) for this lattice are, respectively
(A)
\(\frac{2\pi}{a}(\hat{x}-\frac{\hat{y}}{\sqrt{3}})\) and \(\frac{4\pi}{a\sqrt{3}}\hat{y}\)
(B)
\(\frac{2\pi}{a}(\hat{x}+\frac{\hat{y}}{\sqrt{3}})\) and \(\frac{4\pi}{a\sqrt{3}}\hat{y}\)
(C)
\(\frac{2\pi}{a\sqrt{3}}\hat{x}\) and \(\frac{4\pi}{a}(\frac{\hat{x}}{\sqrt{3}}+\hat{y})\)
(D)
\(\frac{2\pi}{a\sqrt{3}}\hat{x}\) and \(\frac{4\pi}{a}(\frac{\hat{x}}{\sqrt{3}}-\hat{y})\)
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:9 GATE-2018
For the given unit cells of a two dimensional square lattice, which option lists all the primitive cells?

(A)
1 and 2
(B)
1, 2 and 3
(C)
1, 2, 3 and 4
(D)
1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:10 GATE-2019
Consider a three-dimensional crystal of \(N\) inert gas atoms. The total energy is given by \(U(R)=2N\epsilon\left[p\left(\frac{\sigma}{R}\right)^{12}-q\left(\frac{\sigma}{R}\right)^6\right]\), where \(p=12.13, q=14.45\), and \(R\) is the nearest neighbour distance between two atoms. The two constants, \(\epsilon\) and \(R\), have the dimensions of energy and length, respectively. The equilibrium separation between two nearest neighbour atoms in units of \(\sigma\) (rounded off to two decimal places) is ________________
Check Answer
Ans 1.07-1.11
Q.No:11 GATE-2020
The number of distinct ways the primitive unit cell can be constructed for the two dimensional lattice as shown in the figure is ___________________.
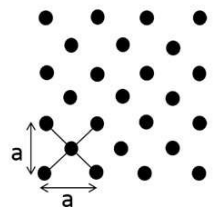
Check Answer
Ans 5
Q.No:12 GATE-2020
Consider a simple cubic monoatomic Bravais lattice which has a basis with vectors \(\vec{r}_1=0, \vec{r}_2=\frac{a}{4}(\hat{x}+\hat{y}+\hat{z})\), \(a\) is the lattice parameter. The Bragg reflection is observed due to the change in the wave vector between he incident and the scattered beam as given by \(\vec{K}=n_1 \vec{G}_1+n_2 \vec{G}_2+n_3 \vec{G}_3\), where \(\vec{G}_1, \vec{G}_2\), and \(\vec{G}_3\) are primitive reciprocal lattice vectors. For \(n_1=3, n_2=3\) and \(n_3=2\), the geometrical structure factor is __________.
Check Answer
Ans 2
Q.No:13 GATE-2021
As shown in the figure, X-ray diffraction pattern is obtained from a diatomic chain of atoms \(P\) and \(Q\). The diffraction condition is given by \(a\cos{\theta}=n\lambda\), where \(n\) is the order of the diffraction peak. Here, \(a\) is the lattice constant and \(\lambda\) is the wavelength of the X-rays. Assume that atomic form factors and resolution of the instrument do not depend on \(\theta\). Then, the intensity of the diffraction peaks is
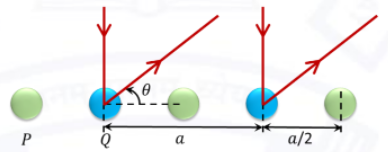
(A)
lower for even values of \(n\), when compared to odd values of \(n\)
(B)
lower for odd values of \(n\), when compared to even values of \(n\)
(C)
zero for odd values of \(n\)
(D)
zero for even values of \(n\)
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:14 GATE-2021
A two-dimensional square lattice has lattice constant \(a\). \(k\) represents the wavevector in reciprocal space. The coordinates \((k_x, k_y)\) of reciprocal space where band gap(s) can occur, are
(A)
\((0, 0)\)
(B)
\(\left(\pm \frac{\pi}{a}, \pm \frac{\pi}{a}\right)\)
(C)
\(\left(\pm \frac{\pi}{a}, \pm \frac{\pi}{1.3a}\right)\)
(D)
\(\left(\pm \frac{\pi}{3a}, \pm \frac{\pi}{a}\right)\)
Check Answer
Option B,C,D
Q.No:15 GATE-2022
In an X-Ray diffraction experiment on a solid with FCC structure, five diffraction peaks corresponding to (111), (200), (220), (311) and (222) planes are observed using \(1.54\) Angstrom X-rays. On using \(3\) Angstrom X-rays on the same solid, the number of observed peaks will be _________
Check Answer
Ans 1
Q.No:16 GATE-2022
The X-ray diffraction pattern of a monatomic cubic crystal with rigid spherical atoms of radius \(1.56A \) shows several Bragg reflections of which the reflection appearing at the lowest \(2\theta\) value is from (\(111\)) plane. If the wavelength of X-ray used is \(0.78 A \), the Bragg angle (in \(2\theta\), rounded off to one decimal place) corresponding to this reflection and the crystal structure, respectively, are
(A) \(21.6^\circ\) and body centered cubic
(B) \(17.6^\circ\) and face centered cubic
(C) \(10.8^\circ\) and body centered cubic
(D) \(8.8^\circ\) and face centered cubic
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:17 GATE-2025
For a two-dimensional hexagonal lattice with lattice constant \(a\),
the atomic density is
A) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}\,a^{2}}\)
B) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{6}\,a^{2}}\)
C) \(\frac{4}{3\sqrt{3}\,a^{2}}\)
D) \(\frac{1}{3\sqrt{3}\,a^{2}}\)
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:18 GATE-2025
Consider a crystal that has a basis of one atom. Its primitive vectors are
\[
\vec a_1 = a\,\hat{i}, \qquad
\vec a_2 = a\,\hat{j}, \qquad
\vec a_3 = \frac{a}{2}(\hat{i} + \hat{j} + \hat{k}),
\]
where \(\hat{i}, \hat{j}, \hat{k}\) are the unit vectors in the \(x, y, z\) directions
of the Cartesian coordinate system and \(a\) is a positive constant.
Which one of the following is the correct option regarding the type of the Bravais
lattice?
A) It is BCC and the volume of the primitive cell is \(\frac{a^{3}}{2}\).
B) It is FCC and the volume of the primitive cell is \(\frac{a^{3}}{4}\).
C) It is BCC and the volume of the primitive cell is \(\frac{a^{3}}{8}\).
D) It is FCC and the volume of the primitive cell is \(a^{3}\).
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:19 GATE-2025
Powder X-ray diffraction pattern of a cubic solid with lattice constant \(a\)
has the \((111)\) diffraction peak at \(\theta = 30^\circ\).
If the lattice expands such that the lattice constant becomes \(1.25a\),
the angle (in degrees) corresponding to the \((111)\) peak changes to
\(\sin^{-1}\!\left(\frac{1}{n}\right)\).
The value of \(n\) (rounded off to one decimal place) is
