Q.No:1 JEST-2012
An observer in an inertial frame finds that at a point \(P\) the electric field vanishes but the magnetic field does not. This implies that in any other inertial frame the electric field \(\vec{E}\) and the magnetic field \(\vec{B}\) satisfy
(a)
\(|\vec{E}|^2=|\vec{B}|^2\)
(b)
\(\vec{E}\cdot \vec{B}=0\)
(c)
\(\vec{E}\times \vec{B}=0\)
(d)
\(\vec{E}=0\)
Check Answer
Option a
Q.No:2 JEST-2012
A circular conducting ring of radius \(R\) rotates with constant angular velocity \(\omega\) about its diameter placed along the \(x\)-axis. A uniform magnetic field \(B\) is applied along the \(y\)-axis. If at time \(t=0\) the ring is entirely in the \(xy\)-plane, the emf induced in the ring at time \(t>0\) is
(a)
\(B\omega^2 \pi R^2 t\)
(b)
\(B\omega \pi R^2 \tan{(\omega t)}\)
(c)
\(B\omega \pi R^2 \sin{(\omega t)}\)
(d)
\(B\omega \pi R^2 \cos{(\omega t)}\)
Check Answer
Option c
Q.No:3 JEST-2012
A small magnet is dropped down a long vertical copper tube in a uniform gravitational field. After a long time, the magnet
(a)
attains a constant velocity
(b)
moves with a constant acceleration
(c)
moves with a constant deceleration
(d)
executes simple harmonic motion
Check Answer
Option a
Q.No:4 JEST-2012
A time-dependent magnetic field \(\vec{B}(t)\) is produced in a circular region of space, infinitely long and of radius \(R\). The magnetic field is given as \(\vec{B}=B_0 t\hat{z}\) for \(0\leq rR\), where \(B_0\) is a positive constant. The electric field for \(r>R\) is
(a)
\(\frac{B_0 R^2}{r}\hat{r}\)
(b)
\(\frac{B_0 R^2}{2r}\hat{\theta}\)
(c)
\(-\frac{B_0 R^2}{r}\hat{r}\)
(d)
\(-\frac{B_0 R^2}{2r}\hat{\theta}\)
Check Answer
Option d
Q.No:5 JEST-2013
At `equilibrium' there can not be any free charge inside a metal. However, if you forcibly put charge in the interior then it takes some finite time to `disappear', i.e. move to the surface. If the conductivity, \(\sigma\), of a metal is \(10^6 (\Omega m)^{-1}\) and the dielectric constant \(\epsilon_0=8.85\times 10^{-12} Farad/m\), this time will be approximately:
(a)
\(10^{-5} sec\)
(b)
\(10^{-11} sec\)
(c)
\(10^{-9} sec\)
(d)
\(10^{-17} sec\)
Check Answer
Option d
Q.No:6 JEST-2013
An electromagnetic wave of frequency \(\omega\) travels in the \(x\)-direction through vacuum. It is polarized in the \(y\)-direction and the amplitude of the electric field is \(E_0\). With \(k=\omega/c\) where \(c\) is the speed of light in vacuum, the electric and the magnetic fields are then conventionally given by
(a)
\(\vec{E}=E_0\cos{(ky-\omega t)}\hat{x}\) and \(\vec{B}=\frac{E_0}{c}\cos{(ky-\omega t)}\hat{z}\)
(b)
\(\vec{E}=E_0\cos{(kx-\omega t)}\hat{y}\) and \(\vec{B}=\frac{E_0}{c}\cos{(kx-\omega t)}\hat{z}\)
(c)
\(\vec{E}=E_0\cos{(kx-\omega t)}\hat{z}\) and \(\vec{B}=\frac{E_0}{c}\cos{(kx-\omega t)}\hat{y}\)
(d)
\(\vec{E}=E_0\cos{(kx-\omega t)}\hat{x}\) and \(\vec{B}=\frac{E_0}{c}\cos{(ky-\omega t)}\hat{y}\)
Check Answer
Option b
Q.No:7 JEST-2013
The electric and magnetic fields caused by an accelerated charged particle are found to scale as \(E\propto r^{-n}\) and \(B\propto r^{-m}\) at large distances. What are the values of \(n\) and \(m\)?
(a)
\(n=1, m=2\)
(b)
\(n=2, m=1\)
(c)
\(n=1, m=1\)
(d)
\(n=2, m=2\)
Check Answer
Option c
Q.No:8 JEST-2014
An electron is executing simple harmonic motion along the \(y\)-axis in right handed coordinate system. Which of the following statements is true for emitted radiation?
(a)
The radiation will be most intense in \(xz\) plane
(b)
The radiation will be most intense in \(xy\) plane
(c)
The radiation will violate causality
(d)
The electron's rest mass energy will reduce due to radiation loss
Check Answer
Option a
Q.No:9 JEST-2015
The skin depth of a metal is dependent on the conductivity (\(\sigma\)) of the metal and the angular frequency (\(\omega\)) of the incident field. For a metal of high conductivity, which of the following relations is correct? (Assume that \(\sigma \gg \in \omega\), where \(\in\) is the electrical permittivity of the medium.)
(a)
\(d\propto \sqrt{\frac{\sigma}{\omega}}\)
(b)
\(d\propto \sqrt{\frac{1}{\sigma\omega}}\)
(c)
\(d \propto \sqrt{\sigma\omega}\)
(d)
\(d\propto \sqrt{\frac{\omega}{\sigma}}\)
Check Answer
Option b
Q.No:10 JEST-2015
The approximate force exerted on a perfectly reflecting mirror by an incident laser beam of power \(10 mW\) at normal incidence is
(a)
\(10^{-13} N\)
(b)
\(10^{-11} N\)
(c)
\(10^{-9} N\)
(d)
\(10^{-15} N\)
Check Answer
Option b
Q.No:11 JEST-2015
Which of the following expressions represents an electric field due to a time varying magnetic field?
(a)
\(K(x\hat{x}+y\hat{y}+z\hat{z})\)
(b)
\(K(x\hat{x}+y\hat{y}-z\hat{z})\)
(c)
\(K(x\hat{x}-y\hat{y})\)
(d)
\(K(y\hat{y}-x\hat{y}+2z\hat{z})\)
Check Answer
Option d
Q.No:12 JEST-2016
The maximum relativistic kinetic energy of \(\beta\) particles from a radioactive nucleus is equal to the rest mass energy of the particle. A magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the beam of \(\beta\) particles, which bends it to a circle of radius \(R\). The field is given by:
(A)
\(3m_0 c/eR\)
(B)
\(\sqrt{2}m_0 c/eR\)
(C)
\(\sqrt{3}m_0 c/eR\)
(D)
\(\sqrt{3}m_0 c/2eR\)
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:13 JEST-2016
How much force does light from a \(1.8 W\) laser exert when it is totally absorbed by an object?
(A)
\(6.0\times 10^{-9} N\)
(B)
\(0.6\times 10^{-9} N\)
(C)
\(6.0\times 10^{-8} N\)
(D)
\(4.8\times 10^{-9} N\)
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:14 JEST-2016
Self inductance per unit length of a long solenoid of radius \(R\) with \(n\) turns per unit length is:
(A)
\(\mu_0 \pi R^2 n^2\)
(B)
\(2\mu_0 \pi R^2 n\)
(C)
\(2\mu_0 \pi R^2 n^2\)
(D)
\(\mu_0 \pi R^2 n\)
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:15 JEST-2017
Consider magnetic vector potential \(\vec{A}\) and scalar potential \(\Phi\) which define the magnetic field \(\vec{B}\) and electric field \(\vec{E}\). If one adds \(-\vec{\nabla}\lambda\) to \(\vec{A}\) for a well-defined \(\lambda\), then what should be added to \(\Phi\) so that \(\vec{E}\) remains unchanged up to an arbitrary function of time, \(f(t)\)?
(A)
\(\frac{\partial \lambda}{\partial t}\)
(B)
\(-\frac{\partial \lambda}{\partial t}\)
(C)
\(\frac{1}{2} \frac{\partial \lambda}{\partial t}\)
(D)
\(-\frac{1}{2} \frac{\partial \lambda}{\partial t}\)
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:16 JEST-2017
A plane electromagnetic wave propagating in air with \(\vec{E}=(8\hat{i}+6\hat{j}+5\hat{k})e^{i(\omega t+3x-4y)}\) is incident on a perfectly conducting slab positioned at \(x=0\). \(\vec{E}\) field of the reflected wave is
(A)
\((-8\hat{i}-6\hat{j}-5\hat{k})e^{i(\omega t+3x+4y)}\).
(B)
\((-8\hat{i}+6\hat{j}-5\hat{k})e^{i(\omega t+3x+4y)}\).
(C)
\((-8\hat{i}+6\hat{j}-5\hat{k})e^{i(\omega t-3x-4y)}\).
(D)
\((-8\hat{i}-6\hat{j}-5\hat{k})e^{i(\omega t-3x-4y)}\).
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:17 JEST-2018
An electromagnetic wave of wavelength \(\lambda\) is incident normally on a dielectric slab of thickness \(t\). If \(K\) is the dielectric constant of the slab, the change in phase of the emergent wave compared with the case of propagation in the absence of the dielectric slab is
(A)
\(\sqrt{K}-1\)
(B)
\(2\pi\)
(C)
\(\frac{2\pi t}{\lambda}\)
(D)
\(\frac{2\pi t}{\lambda}(\sqrt{K}-1)\)
Check Answer
Option D
Q.No:18 JEST-2018
Two conductors are embedded in a material of conductivity \(10^{-4} ohm-m\) and dielectric constant \(\epsilon=80\epsilon\). The resistance between the two conductors is \(10^6 ohm\). What is the capacitance (in pF) between the two conductors? Ignore the decimal part of the answer.
Check Answer
Ans 30
Q.No:19 JEST-2018
Two parallel rails of a railroad track are insulated from each other and from the ground. The distance between the rails is \(1\) meter. A voltmeter is electrically connected between the rails. Assume the vertical component of the earth's magnetic field to be \(0.2\) gauss. What is the voltage developed between the rails when a train travels at a speed of \(180 km/h\) along the track? Give the answer in milli-volts.
Check Answer
Ans 1
Q.No:20 JEST-2018
The elastic wave on a stretched rectangular membrane of size \(L\times 2L\) in the \(x\)-\(y\) plane is described by the function
\[
A\sin{\frac{\pi x}{L}}\sin{\frac{\pi y}{L}}\cos{(\omega t+\phi)},
\]
where \(A\) and \(\phi\) are constants. The speed of the elastic waves is \(v\). The angular frequency \(\omega\) is
(A)
\(\frac{\sqrt{5}\pi v}{L}\)
(B)
\(\frac{\sqrt{2}\pi v}{L}\)
(C)
\(\frac{\sqrt{5}\pi v}{2L}\)
(D)
\(\frac{\sqrt{17}\pi v}{2L}\)
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:21 JEST-2019
A very long solenoid (axis along \(z\) direction) of \(n\) turns per unit length carries a current which increases linearly with time, \(i=Kt\). What is the magnetic field inside the solenoid at a given time \(t\)?
(A)
\(\mathbf{B}=\mu_0 nKt\hat{\mathbf{z}}\)
(B)
\(\mathbf{B}=\mu_0 nK\hat{\mathbf{z}}\)
(C)
\(\mathbf{B}=\mu_0 nKt(\hat{\mathbf{x}}+\hat{\mathbf{y}})\)
(D)
\(\mathbf{B}=\mu_0 cnKt\hat{\mathbf{z}}\)
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:22 JEST-2019
The magnetic field (Gaussian units) in an empty space is described by
\[
\mathbf{B}=B_0\exp{(ax)}\sin{(ky-\omega t)}\hat{\mathbf{z}}.
\]
What is the \(y\)-component of the electric field?
(A)
\(-\frac{ac}{\omega}B_0 \sin{(ky-\omega t)}\)
(B)
\(-\frac{ac}{\omega}B_0 \exp{(ax)} \cos{(ky-\omega t)}\)
(C)
\(-B_0 \sin{(ky-\omega t)}\)
(D)
\(0\)
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:23 JEST-2019
A circular metal loop of radius \(a=1 m\) spins with a constant angular velocity \(\omega=20\pi rad/s\) in a magnetic field \(B=3\) Tesla, as shown in the figure. The resistance of the loop is \(10\) Ohms. Let \(P\) be the power dissipated in one complete cycle. What is the value of \(\frac{P}{\pi^3}\) in Watts?

Check Answer
Ans
Q.No:24 JEST-2020
Two rails of a railroad track are insulated from each other and from the ground, and are connected by a millivoltmeter. What is the reading of the millivoltmeter when a train travels at the speed of \(90 km/hr\) down the track? Assume that the vertical component of the earth's magnetic field is \(0.2\) gauss and that the tracks are separated by two meters. Use \(1 gauss=10^{-4} Tesla=10^{-4} V\cdot sec/m^2\).
(A)
\(10\)
(B)
\(1\)
(C)
\(0.2\)
(D)
\(180\)
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:25 JEST-2020
An electromagnetic field is given by
\[
\vec{E}(\vec{r}, t)=-\frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_0}\frac{q}{r^2}\theta(vt-r)\hat{r}, \vec{B}(\vec{r}, t)=0
\]
where
\[
\theta(x)=
\left\{
\begin{array}{ll}
1 & \text{for }x>0 \\
0 & \text{for }x\leq 0
\end{array}
\right.
\]
The corresponding charge density \(\rho\) and current density \(\vec{J}\) are given by
(A)
\(\rho=-q\delta^3(\vec{r})\theta(vt-r)+\frac{q}{4\pi r^2}\theta(vt-r); \vec{J}=0\)
(B)
\(\rho=-q\delta^3(\vec{r})\theta(vt-r); \vec{J}=0\)
(C)
\(\rho=\frac{q}{4\pi r^2}\theta(vt-r); \vec{J}=\frac{qv}{4\pi r^2}\delta(vt-r)\hat{r}\)
(D)
\(\rho=-q\delta^3(\vec{r})\theta(vt-r)+\frac{q}{4\pi r^2}\delta(vt-r); \vec{J}=\frac{qv}{4\pi r^2}\delta(vt-r)\hat{r}\)
Check Answer
Option D
Q.No:26 JEST-2020
A laser has output power of \(150 mW\) with beam diameter of \(2 mm\) at a wavelength \(630 nm\). What is the value of the electric field in units of V/m is? Use Coulomb's constant, \(1/(4\pi \epsilon_0)=9\times 10^9 N~m^2 C^{-2}\).
Check Answer
Ans 6000
Q.No:27 JEST-2021
Consider a sphere of radius \(R\) containing a charge with volume density \(\rho(r)=4\pi \epsilon_0 \alpha/r\). The charge is zero outside the sphere. The electromagnetic potentials (\(\phi\) and \(\vec{\mathbf{A}}\)) inside the sphere may be written in many ways. Which of the following values of \(\phi\) and \(\vec{\mathbf{A}}\) inside the sphere describe the situation correctly?
(A)
\(\phi=0, \vec{\mathbf{A}}=-2\pi \alpha t\hat{\mathbf{r}}\)
(B)
\(\phi=2\pi \alpha r, \vec{\mathbf{A}}=0\)
(C)
\(\phi=0, \vec{\mathbf{A}}=-\pi \alpha t\hat{\mathbf{r}}\)
(D)
\(\phi=\pi \alpha r, \vec{\mathbf{A}}=0\)
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:28 JEST-2022
A circularly polarized laser of power \(P\) is incident on a particle of mass \(m\). The particle, which was initially at rest, completely absorbs the incident radiation. The kinetic energy of the particle as a function of time \(t\) is given by
(a)
\(\frac{2}Pt\left(\frac{Pt}{mc^2}+1\right)\)
(b)
\(\frac{2}Pt\left(\frac{Pt}{mc^2}-1\right)\)
(c)
\(\frac{P^2 t^2}{2mc^2}\)
(d)
\(\frac{Pt}{2}\)
Check Answer
Option a
Q.No:29 JEST-2023
A beam of light of intensity \(I_0\) = 120 W/\(m^2\) is incident on the optical system shown in the figure. \(BS_1, BS_2, BS_3\), and \(BS_4\) are ideal, 50/50 beamsplitters (reflects \(50\%\) and transmits \(50\%\)
of incident light intensity). \(I_1, I_2, I_3\), and \(I_4\) are the total intensities measured by detectors. What will be the intensity \(I_3\)?
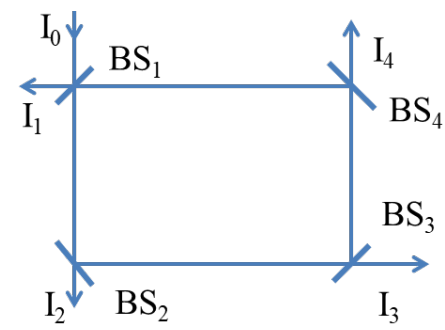
(a) 32 W/\(m^2\)
(b) 20 W/\(m^2\)
(c) 16 W/\(m^2\)
(d) 12 W/\(m^2\)
Check Answer
Option c
Q.No:29 JEST-2024
A semi-infinite, thin wire extending from \( -\infty \) to zero along the \( z \)-axis carries a constant current \( I \) in the positive \( z \)-direction. The wire is charge-neutral except at \( z = 0 \), where the inflowing charge is accumulated. What is the absolute value of the line integral
\[
\frac{4}{\mu_0 I} \oint \vec{B} \cdot d\vec{l}
\]
along the circle \( x^2 + y^2 = 1 \)? \( \vec{B} \) is the magnetic field and \( \mu_0 \) is the permeability in free space. Assume that the accumulated charge at \( z = 0 \) is a point charge.
Check Answer
Ans 2
Q.No:30 JEST-2025
A ray of light is incident on a glass cube of refractive index \(1.414\) as shown in the figure. Find the angle of incidence \(\theta_{i}\), such that the ray grazes down the side of the glass cube.
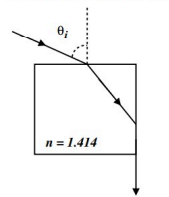
a) \(\pi/4\)
b) \(\pi/3\)
c) \(0\)
d) \(\pi/2\)
Check Answer
Option d
Q.No:31 JEST-2025
For a plane electromagnetic wave propagating with wave vector \(\vec{k}\) in a homogeneous and isotropic medium, which of the following holds?
a) \(\vec{E}\times\vec{B}=\vec{0}\)
b)\(\vec{k}\cdot(\vec{E}\times\vec{B})=0\)
c) None of the others.
d) \(\vec{E}\cdot\vec{B}=0\)
