Q.No:1 GATE-2012
Consider the wavefunction \(\Psi=\psi(\vec{r}_1, \vec{r}_2)\chi_s\) for a fermionic system consisting of two spin-half particles. The spatial part of the wavefunction is given by,
\[
\psi(\vec{r}_1, \vec{r}_2)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}[\phi_1(\vec{r}_1)\phi_2(\vec{r}_2)+\phi_2(\vec{r}_1)\phi_1(\vec{r}_2)]
\]
where \(\phi_1\) and \(\phi_2\) are single particle states. The spin part \(\chi_s\) of the wavefunction with spin states \(\alpha(+1/2)\) and \(\beta(-1/2)\) should be
(A)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(\alpha\beta+\beta\alpha)\)
(B)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(\alpha\beta-\beta\alpha)\)
(C)
\(\alpha\alpha\)
(D)
\(\beta\beta\)
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:2 GATE-2014
The ground state and the first excited state wave functions of a one dimensional infinite potential well are \(\psi_1\) and \(\psi_2\), respectively. When two spin-up electrons are placed in this potential, which one of the following, with \(x_1\) and \(x_2\) denoting the position of the two electrons, correctly represents the space part of the ground state wave function of the system?
(A)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}[\psi_1(x_1)\psi_2(x_1)-\psi_1(x_2)\psi_2(x_2)]\)
(B)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}[\psi_1(x_1)\psi_2(x_1)+\psi_1(x_2)\psi_2(x_2)]\)
(C)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}[\psi_1(x_1)\psi_2(x_2)+\psi_1(x_2)\psi_2(x_1)]\)
(D)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}[\psi_1(x_1)\psi_2(x_2)-\psi_1(x_2)\psi_2(x_1)]\)
Check Answer
Option D
Q.No:3 GATE-2015
The Pauli matrices for three spin-\(1/2\) particles are \(\vec{\sigma}_1, \vec{\sigma}_2\), and \(\vec{\sigma}_3\), respectively. The dimension of the Hilbert space required to define an operator \(\hat{O}=\vec{\sigma}_1\cdot \vec{\sigma}_2\times \vec{\sigma}_3\) is ________________.
Check Answer
Ans 8
Q.No:4 GATE-2015
Consider a system of eight non-interacting, identical quantum particles of spin-\(3/2\) in a one dimensional box of length \(L\). The minimum excitation energy of the system, in units of \(\frac{\pi^2 \hbar^2}{2mL^2}\) is _____________.
Check Answer
Ans 5
Q.No:5 GATE-2016
A two-dimensional square rigid box of side \(L\) contains six non-interacting electrons at \(T=0 K\). The mass of the electron is \(m\). The ground state energy of the system of electrons, in units of \(\frac{\pi^2 \hbar^2}{2mL^2}\) is ____________.
Check Answer
Ans 24
Q.No:6 GATE-2019
For a spin \(\frac{1}{2}\) particle, let \(|\uparrow\rangle\) and \(|\downarrow\rangle\) denote its spin up and spin down states, respectively. If \(|a\rangle=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(|\uparrow\rangle |\downarrow\rangle+|\downarrow\rangle |\uparrow\rangle)\) and \(|b\rangle=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(|\uparrow\rangle |\downarrow\rangle-|\downarrow\rangle |\uparrow\rangle)\) are composite states of two such particles, which of the following statements is true for their total spin \(S\)?
(A)
\(S=1\) for \(|a\rangle\), and \(|b\rangle\) is not an eigenstate of the operator \(\hat{S}^2\)
(B)
\(|a\rangle\) is not an eigenstate of the operator \(\hat{S}^2\), and \(S=0\) for \(|b\rangle\)
(C)
\(S=0\) for \(|a\rangle\), and \(S=1\) for \(|b\rangle\)
(D)
\(S=1\) for \(|a\rangle\), and \(S=0\) for \(|b\rangle\)
Check Answer
Option D
Q.No:7 GATE-2021
Three non-interacting bosonic particles of mass \(m\) each, are in a one-dimensional infinite potential well of width \(a\). The energy of the third excited state of the system is \(x\times \frac{\hbar^2 \pi^2}{ma^2}\). The value of \(x\) (in integer) is _____.
Check Answer
Ans 5-6
Q.No:8 GATE-2025
A system of five identical, non-interacting particles with mass \(m\) and spin \(\frac{3}{2}\) is confined to a one-dimensional potential well of length \(L\). If the lowest energy of the system is
\[
N \frac{\pi^{2}\hbar^{2}}{2mL^{2}},
\]
the value of \(N\) (in integer) is ___
Check Answer
Ans 8
Q.No:1 CSIR Dec-2018
Three identical spin-\(\frac{1}{2}\) particles of mass \(m\) are confined to a one-dimensional box of length \(L\), but are otherwise free. Assuming that they are non-interacting, the energies of the lowest two energy eigenstates, in units of \(\frac{\pi^2 \hbar^2}{2mL^2}\), are
(1)
\(3\) and \(6\)
(2)
\(6\) and \(9\)
(3)
\(6\) and \(11\)
(4)
\(3\) and \(9\)
Check Answer
Option 2
Q.No:2 CSIR Dec-2019
Two spin \(\frac{1}{2}\) fermions of mass \(m\) are confined to move in a one-dimensional infinite potential well of width \(L\). If the particles are known to be in a spin triplet state, the ground state energy of the system (in units of \(\frac{\hbar^2 \pi^2}{2mL^2}\)) is
(1)
\(8\)
(2)
\(2\)
(3)
\(3\)
(4)
\(5\)
Check Answer
Option 4
Q.No:3 Assam CSIR Dec-2019
The number density of a mono-atomic gas is \(10^{18} m^{-3}\). The temperature at which the thermal de Broglie wavelength of the atoms (which have mass \(m\)) equals the average inter-atomic separation, is
(1)
\(\frac{h^2}{2\pi mk_B}\times 10^{12} K\)
(2)
\(\frac{h^2}{2\pi mk_B}\times 10^{10} K\)
(3)
\(\frac{h^2}{2\pi mk_B}\times 10^{9} K\)
(4)
\(\frac{h^2}{2\pi mk_B}\times 10^{11} K\)
Check Answer
Option 4
Q.No: 4 Assam CSIR Dec-2019
The coordinates of two identical particles of spin \(0\) in one dimension are \(x_1\) and \(x_2\), respectively. Which of the following functions is an admissible wavefunction for the two-particle system?
(1)
\(\frac{1}{2\pi a} e^{-\frac{1}{2a^2}(x_1^2+\frac{x_2^2}{4})}\)
(2)
\(\frac{1}{\pi a} e^{i(k_1 x_1+k_2 x_2)} e^{-\frac{1}{2a^2}(x_1^2+x_2^2)}\)
(3)
\(\frac{1}{2\pi a} e^{i(k_1 x_1+k_2 x_2)} e^{-\frac{1}{2a^2}(x_1^2+\frac{x_2^2}{4})}\)
(4)
\(\frac{1}{21\pi a^5} (x_1-x_2)^2 e^{-\frac{1}{2a^2}(x_1^2+x_2^2)}\)
Check Answer
Option 4
Q.No: 6 CSIR June -2023
A one-dimensional box contains one spin \(0\) particle and four spin \(\frac{1}{2}\) particles. All particles have the same mass, hence the single particle energies are \(E_n=n^2 E\), \(n=1, 2, 3, \cdots\). The energies of the ground and the first excited states of the system of particles are, respectively,
(1)
\(10E\) and \(12E\)
(2)
\(11E\) and \(20E\)
(3)
\(11E\) and \(14E\)
(4)
\(10E\) and \(13E\)
Check Answer
Option 3
Q.No:5 Assam CSIR Dec-2019
Two distinguishable non-interacting particles, each of mass \(m\) are in a one-dimensional infinite square well in the interval \([0,a]\). If \(x_1\) and \(x_2\) are position operators of the two particles, the expectation value \(\langle x_1 x_2\rangle\) in the state in which one particle is in the ground state and the other one is in the first excited state, is
1) \(\frac{1}{2}a^2\)
2) \(\frac{1}{2}\pi^2 a^2\)
3) \(\frac{1}{4}a^2\)
4) \(\frac{1}{4}\pi^2 a^2\)
Check Answer
Option 3
Q.No:6 CSIR Dec-2024
Two non-interacting identical spin-\(\frac{1}{2}\) particles, each of mass \(m\), are placed in a two-dimensional infinite square well of side \(L\).
The single-particle spatial wavefunction is
\[
\varphi_{n_x,n_y}(x,y)=\frac{2}{L}\sin\left(\frac{n_x \pi x}{L}\right)\sin\left(\frac{n_y \pi y}{L}\right)
\]
where \(n_x\) and \(n_y\) are positive integers.
If the particles are in a total spin state \(|j=1,m=0\rangle\), the lowest possible energy eigenvalue is
1) \(\frac{5\hbar^{2}\pi^{2}}{2mL^{2}}\)
2) \(\frac{\hbar^{2}\pi^{2}}{mL^{2}}\)
3) \(\frac{2\hbar^{2}\pi^{2}}{mL^{2}}\)
4) \(\frac{7\hbar^{2}\pi^{2}}{2mL^{2}}\)
Check Answer
Option 4
Q.No:7 CSIR June-2025
A system consists of two non-interacting identical spin-\(\frac{1}{2}\) particles.
The spatial wave functions for the individual particles are given by
\(\varphi_{1}(x)\) and \(\varphi_{2}(x)\).
Let \(x_{1}\) and \(x_{2}\) denote the positions of the particles respectively.
The total wave function of the system (not necessarily normalized) can be
1) \(\left[\varphi_{1}(x_{1})\varphi_{2}(x_{2}) - \varphi_{2}(x_{1})\varphi_{1}(x_{2})\right]
\left(\vert\uparrow\rangle_{1}\vert\downarrow\rangle_{2}
+ \vert\downarrow\rangle_{1}\vert\uparrow\rangle_{2}\right)\)
2) \(\left[\varphi_{1}(x_{1})\varphi_{1}(x_{2}) + \varphi_{2}(x_{1})\varphi_{2}(x_{2})\right]
\vert\uparrow\rangle_{1}\vert\uparrow\rangle_{2}\)
3) \(\varphi_{1}(x_{1})\varphi_{2}(x_{2})
\vert\uparrow\rangle_{1}\vert\uparrow\rangle_{2}\)
4) \(\left[\varphi_{1}(x_{1})\varphi_{2}(x_{2}) - \varphi_{2}(x_{1})\varphi_{1}(x_{2})\right]
\left[\vert\uparrow\rangle_{1}\vert\downarrow\rangle_{2}
- \vert\downarrow\rangle_{1}\vert\uparrow\rangle_{2}\right]\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No: 1 JEST-2012
The ground state energy of \(5\) identical spin-\(1/2\) particles which are subject to a one-dimensional simple harmonic oscillator potential of frequency \(\omega\) is
(a)
\((15/2)\hbar \omega\)
(b)
\((13/2)\hbar \omega\)
(c)
\((1/2)\hbar \omega\)
(d)
\(5\hbar \omega\)
Check Answer
Option b
Q.No: 2 JEST-2012
The spatial part of a two-electron state is symmetric under exchange. If \(|\uparrow\rangle\) and \(|\downarrow\rangle\) represent the spin-up and spin-down states respectively of each particle, the spin-part of the two-particle state is
(a)
\(|\uparrow\rangle |\uparrow\rangle\)
(b)
\(|\uparrow\rangle |\downarrow\rangle\)
(c)
\((|\downarrow\rangle |\uparrow\rangle-|\uparrow\rangle |\downarrow\rangle)/\sqrt{2}\)
(d)
\((|\downarrow\rangle |\uparrow\rangle+|\uparrow\rangle |\downarrow\rangle)/\sqrt{2}\)
Check Answer
Option c
Q.No: 3 JEST-2013
Two electrons are confined in a one dimensional box of length \(L\). The one-electron states are given by \(\psi_n(x)=\sqrt{2/L}\sin{(n\pi x/L)}\). What would be the ground state wave function \(\psi(x_1, x_2)\) if both electrons are arranged to have the same spin state?
(a)
\(\psi(x_1, x_2)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left[\frac{2}{L}\sin{\left(\frac{\pi x_1}{L}\right)}\sin{\left(\frac{2\pi x_2}{L}\right)}+\frac{2}{L}\sin{\left(\frac{2\pi x_1}{L}\right)}\sin{\left(\frac{\pi x_2}{L}\right)}\right]\)
(b)
\(\psi(x_1, x_2)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left[\frac{2}{L}\sin{\left(\frac{\pi x_1}{L}\right)}\sin{\left(\frac{2\pi x_2}{L}\right)}-\frac{2}{L}\sin{\left(\frac{2\pi x_1}{L}\right)}\sin{\left(\frac{\pi x_2}{L}\right)}\right]\)
(c)
\(\psi(x_1, x_2)=\frac{2}{L}\sin{\left(\frac{\pi x_1}{L}\right)}\sin{\left(\frac{2\pi x_2}{L}\right)}\)
(d)
\(\psi(x_1, x_2)=\frac{2}{L}\sin{\left(\frac{2\pi x_1}{L}\right)}\sin{\left(\frac{\pi x_2}{L}\right)}\)
Check Answer
Option b
Q.No: 4 JEST-2014
The lowest quantum mechanical energy of a particle confined in a one-dimensional box of size \(L\) is \(2 eV\). The energy of the quantum mechanical ground state for a system of three non-interacting spin \(\frac{1}{2}\) particles is
(a)
\(6 eV\)
(b)
\(10 eV\)
(c)
\(12 eV\)
(d)
\(16 eV\)
Check Answer
Option c
Q.No: 5 JEST-2019
Consider a system of \(15\) non-interacting spin-polarized electrons. They are trapped in a two dimensional isotropic harmonic oscillator potential \(V(x, y)=\frac{1}{2}m\omega^2(x^2+y^2)\). The angular frequency \(\omega\) is such that \(\hbar\omega=1\) in some chosen unit. What is the ground state energy of the system in the same units?
Check Answer
Ans 55
Q.No: 6 JEST-2021
A one-dimensional box contains three identical particles in the ground state of the system. Find the ratio of total energies of these particles if they were spin-\(1/2\) fermions, to that if they were bosons.
(a)
\(1\)
(b)
\(14/3\)
(c)
\(2\)
(d)
\(1/3\)
Check Answer
Option c
Q.No: 7 JEST-2022
Consider eight electrons confined in a 1D box of length \(d\). What is the minimum total energy for the system allowed by Pauli's exclusion principle?
(a)
\(\frac{15h^2}{2md^2}\)
(b)
\(\frac{15h^2}{4md^2}\)
(c)
\(\frac{30h^2}{md^2}\)
(d)
\(\frac{15h^2}{8md^2}\)
Check Answer
Option a
Q.No: 8 JEST-2022
Consider \(5\) identical spin \(1/2\) particles moving in a \(3\)-dimensional harmonic oscillator potential,
\[
V(r)=\frac{1}{2}m\omega^2 r^2=\frac{1}{2}m\omega^2(x^2+y^2+z^2)
\]
The degeneracy of the ground state of the system is
(a)
\(20\)
(b)
\(7\)
(c)
\(5\)
(d)
\(32\)
Check Answer
Option a
Q.No: 9 JEST-2023
The spatial part of a two-electron state is anti-symmetric under exchange. If \(| \uparrow \rangle\) and \(| \downarrow \rangle\) represent the spin-up and the spin-down states respectively of each electron, the spin part of the two-electron state cannot be: (Q 21 has been cancelled due to typographical error.)
(a) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2} } (| \uparrow \rangle | \downarrow \rangle + (| \uparrow \rangle | \downarrow \rangle)\)
(b) \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2} } (| \uparrow \rangle | \downarrow \rangle - (| \uparrow \rangle | \downarrow \rangle)\)
(c) \(| \uparrow \rangle | \downarrow \rangle \)
(d) \(| \downarrow \rangle | \uparrow \rangle\)
Check Answer
Option c
Q.No: 1 TIFR-2020
A quantum mechanical system consists of a one-dimensional infinite box, as indicated in the figures below.
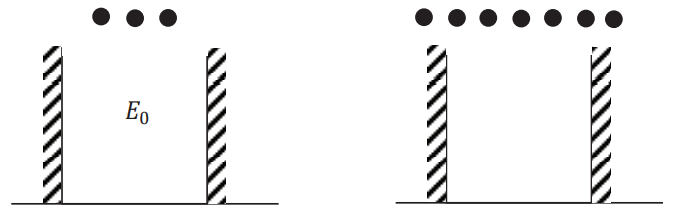
\(3\) (three) identical non-interacting spin-\(\frac{1}{2}\) particles, are first placed in the box, and the ground state energy of the system is found to be \(E_0=18 \hspace{1mm}\text{eV}\). If \(7\) (seven) such identical particles are placed in the box, what will be the ground state energy, in units of \text{eV}?
Check Answer
Ans 132
Q.No:2 TIFR-2020
Three noninteracting particles whose masses are in the ratio \(1:4:16\) are placed together in the same harmonic oscillator potential \(V(x)\).
The degeneracies of the first three energy eigenstates (ordered by increasing energy) will be
(a)
\(1, 1, 1\)
(b)
\(1, 1, 2\)
(c)
\(1, 2, 1\)
(d)
\(1, 2, 2\)
Check Answer
Option b
Q.No:3 TIFR-2022
A system was formed of three spin-\(\frac{1}{2}\) particles A, B and C, respectively and it was prepared in an initial state
\(| \psi \rangle =c_1 | \uparrow \uparrow \uparrow \rangle+c_2 |\uparrow \uparrow \downarrow \rangle +c_3 |\uparrow \downarrow \uparrow \rangle+ |c_4 \uparrow \downarrow \downarrow \rangle \)
\(+c_5 |\downarrow \uparrow \uparrow \rangle+c_6| \downarrow \uparrow \downarrow \rangle+c_7 |\downarrow \downarrow \uparrow \rangle +c_8 | \downarrow \downarrow \downarrow \rangle \)
where the symbols \(|\uparrow \rangle\) and \(|\downarrow \rangle\) indicate states with \(S_z=+ 1/2\) (spin-up) and \(S_z=- 1/2\) (spin-down) respectively.
A measurement was made on the system in the initial state and this identified the spin state of the particle A to be \(|\downarrow \rangle\) (spin-down). Now the expectation value of \(\langle S_z \rangle\) for the
particle C could be calculated as
(a)
\(\frac{|c_5|^2+|c_7|^2-|c_6|^2-|c_8|^2}{|c_5|^2+|c_7|^2+|c_6|^2+|c_8|^2}\)
(b)
\(\frac{c_5+c_7-c_6-c_8}{|c_5|^2+|c_7|^2+|c_6|^2+|c_8|^2}\)
(c)
\(\frac{(|c_5|^*+|c_7|^*-|c_6|^*-|c_8|^*)(c_5+c_7-c_6-c_8)}{|c_5|^2+|c_7|^2+|c_6|^2+|c_8|^2}\)
(d)
\(\frac{(c_5+c_7)^*(c_5+c_7)-(c_6+c_8)^*(c_6+c_8)}{|c_5|^2+|c_7|^2+|c_6|^2+|c_8|^2}\)
