Q.No:1 GATE-2012
In case of a Geiger-Muller (GM) counter, which one of the following statements is CORRECT?
(A)
Multiplication factor of the detector is of the order of \(10^{10}\)
(B)
Type of the particles detected can be identified
(C)
Energy of the particles detected can be distinguished
(D)
Operating voltage of the detector is few tens of Volts
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:2 GATE-2013
Consider the scattering of neutrons by protons at very low energy due to a nuclear potential of range \(r_0\). Given that,
\[
\cot{(kr_0+\delta)}\approx -\frac{\gamma}{k}
\]
where \(\delta\) is the phase shift, \(k\) the wave number and \((-\gamma)\) the logarithmic derivative of the deuteron ground state wave function, the phase shift is
(A)
\(\delta\approx -\frac{k}{\gamma}-kr_0\)
(B)
\(\delta\approx -\frac{\gamma}{k}-kr_0\)
(C)
\(\delta\approx -\frac{\pi}{2}-kr_0\)
(D)
\(\delta\approx -\frac{\pi}{2}-kr_0\)
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:3 GATE-2013
In the \(\beta\) decay process, the transition \(2^{+}\to 3^{+}\), is
(A)
allowed both by Fermi and Gamow-Teller selection rule
(B)
allowed by Fermi and but not by Gamow-Teller selection rule
(C)
not allowed by Fermi but allowed by Gamow-Teller selection rule
(D)
not allowed both by Fermi and Gamow-Teller selection rule
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:4 GATE-2013
The electromagnetic form factor \(F(q^2)\) of a nucleus is given by,
\[
F(q^2)=\exp{\left[-\frac{q^2}{2Q^2}\right]}
\]
where \(Q\) is a constant. Given that
\[
\begin{array}{c}
F(q^2)=\frac{4\pi}{q}\int_{0}^{\infty} rdr\rho(r)\sin{qr} \\
\int d^3 r\rho(r)=1
\end{array}
\]
where \(\rho(r)\) is the charge density, the root mean square radius of the nucleus is given by,
(A)
\(1/Q\)
(B)
\(\sqrt{2}/Q\)
(C)
\(\sqrt{3}/Q\)
(D)
\(\sqrt{6}/Q\)
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:5 GATE-2014
A nucleus \(X\) undergoes a first forbidden \(\beta\)-decay to a nucleus \(Y\). If the angular momentum (\(I\)) and parity (\(P\)), denoted by \(I^P\) as \(\frac{7}{2}^{-}\) for \(X\), which of the following is a possible \(I^P\) value for \(Y\)?
parity (P), denoted by
(A)
\(\frac{1}{2}^{+}\)
(B)
\(\frac{1}{2}^{-}\)
(C)
\(\frac{3}{2}^{+}\)
(D)
\(\frac{3}{2}^{-}\)
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:6 GATE-2015
The mean kinetic energy of a nucleon in a nucleus of atomic weight \(A\) varies as \(A^n\), where \(n\) is __________. (upto two decimal places)
Check Answer
Ans (-0.67 TO -0.66)
Q.No:7 GATE-2015
The atomic masses of \({^{152}_{63} Eu}, {^{152}_{62} Sm}, {^{1}_{1} H}\) and neutron are \(151.921749, 151.919756, 1.007825\) and \(1.008665\) in atomic mass units ( amu), respectively. Using the above information, the \(Q\)-value of the reaction \({^{152}_{63} Eu}+n\to {^{152}_{62} Sm}+p\) is __________ \(\times 10^{-3} amu\) (upto three decimal places)
Check Answer
Ans 2.830-2.835
Q.No:8 GATE-2016
An alpha particle is accelerated in a cyclotron. It leaves the cyclotron with a kinetic energy of \(16 MeV\). The potential difference between the D electrodes is \(50\) kilovolts. The number of revolutions the alpha particle makes in its spiral path before it leaves the cyclotron is ______________.
Check Answer
Ans 80
Q.No:9 GATE-2017
The geometric cross-section of two colliding protons at large energies is very well estimated by the product of the effective sizes of each particle. This is closest to
(A)
\(10 b\)
(B)
\(10 mb\)
(C)
\(10 \mu b\)
(D)
\(10 pb\)
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:10 GATE-2018
For nucleus \({^{164} Er}\), a \(J^{\pi}=2^{+}\) state is at \(90 keV\). Assuming \({^{164} Er}\) to be a rigid rotor, the energy of its \(4^{+}\) state is __________ keV (up to one decimal place).
Check Answer
Ans 297.0-300.1
Q.No:11 GATE-2018
Inside a large nucleus, a nucleon with mass \(939 MeVc^{-2}\) has Fermi momentum \(1.40 fm^{-1}\) at absolute zero temperature. Its velocity is \(Xc\), where the value of \(X\) is __________-(up to two decimal places).
(\(\hbar c=197 MeV-fm\))
Check Answer
Ans 0.28-0.31
Q.No:12 GATE-2018
\(4 MeV\) \(\gamma\)-rays emitted by the de-excitation of \({^{19} F}\) are attributed, assuming spherical symmetry, to the transition of protons from \(1d_{3/2}\) state to \(1d_{5/2}\) state. If the contribution of spin-orbit term to the total energy is written as \(C\langle \vec{l}\cdot \vec{s}\rangle\), the magnitude of \(C\) is ___________ MeV (up to one decimal place).
Check Answer
Ans 1.6
Q.No:13 GATE-2019
A radioactive element \(\mathbf{X}\) has a half-life of \(30\) hours. It decays via alpha, beta and gamma emissions with the branching ratio for beta decay being \(0.75\). The partial half-life for beta decay in unit of hours is ____________.
Check Answer
Ans 40
Q.No:14 GATE-2021
Assume that \({^{13} N}\) (\(Z=7\)) undergoes first forbidden \(\beta^{+}\) decay from its ground state with spin-parity \(J_{i}^{\pi}\), to a final state \(J_{f}^{\pi}\). The possible values for \(J_{i}^{\pi}\) and \(J_{f}^{\pi}\), respectively, are
(A)
\(\frac{1}{2}^{-}, \frac{5}{2}^{+}\)
(B)
\(\frac{1}{2}^{+}, \frac{5}{2}^{+}\)
(C)
\(\frac{1}{2}^{-}, \frac{1}{2}^{-}\)
(D)
\(\frac{1}{2}^{+}, \frac{1}{2}^{-}\)
Check Answer
Option
Q.No:15 GATE-2021
In an experiment, it is seen that an electric-dipole (\(E1\)) transition can connect an initial nuclear state of spin-parity \(J_{i}^{\pi}=2^{+}\) to a final state \(J_{f}^{\pi}\). All possible values of \(J_{f}^{\pi}\) are
(A)
\(1^{+}, 2^{+}\)
(B)
\(1^{+}, 2^{+}, 3^{+}\)
(C)
\(1^{-}, 2^{-}\)
(D)
\(1^{-}, 2^{-}, 3^{-}\)
Check Answer
Option D
Q.No:16 GATE-2021
For the given sets of energy levels of nuclei X and Y whose mass numbers are odd and even, respectively, choose the best suited interpretation.

(A)
Set I: Rotational band of X
Set II: Vibrational band of Y
(B)
Set I: Rotational band of Y
Set II: Vibrational band of X
(C)
Set I: Vibrational band of X
Set II: Rotational band of Y
(D)
Set I: Vibrational band of Y
Set II: Rotational band of X
Check Answer
Option D
Q.No:17 GATE-2021
A linear charged particle accelerator is driven by an alternating voltage source operating at \(10 MHz\). Assume that it is used to accelerate electrons. After a few drift-tubes, the electrons attain a velocity \(2.9\times 10^8 m s^{-1}\). The minimum length of each drift-tube, in m, to accelerate the electrons further (rounded off to one decimal place) is ____________.
Check Answer
Ans 14-15
Q.No:18 GATE-2022
Match the order of \(\beta\)-decays given in the left column to appropriate clause in the right column. Here \(X(I^{\pi})\) and \(Y(I^{\pi})\) are nuclei with intrinsic spin \(I\) and parity \(\pi\).
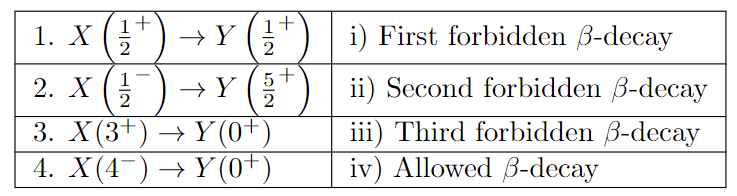
(a)
1-i, 2-ii, 3-iii, 4-iv
(b)
1-iv, 2-i, 3-ii, 4-iii
(c)
1-i, 2-iii, 3-ii, 4-iv
(d)
1-iv, 2-ii, 3-iii, 4-i
Check Answer
Option b
Q.No:19 GATE-2023
A \(^{60} Co\) nucleus emits a \(\beta\)-particle and is converted to \(^{60} Ni^*\) with \(J^P=4^+\), which in turn decays to the \(^{60}Ni\) ground state with \(J^P=0^+\) by emitting two photons in succession, as shown in the figure. Which one of the following statements is CORRECT?

(A)
\(4^+ \to 2^+\) is an electric octupole transition
(B)
\(4^+ \to 2^+\) is a magnetic quadrupole transition
(C)
\(2^+ \to 0^+\) is an electric quadrupole transition
(D)
\(2^+ \to 0^+\) is a magnetic quadrupole transition
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:20 GATE-2023
The Geiger-Muller counter is a device to detect \(\alpha , \beta\) and \(\gamma\) radiations. It is a cylindrical tube filled with monatomic gases like argon, and polyatomic gases such as ethyl alcohol. The inner electrode is along the axis of the cylindrical tube and the outer electrode is the tube. Which of the following statements is(are) CORRECT?
(A)
Argon is used so that ambient light coming from the surroundings do not produce any signal in the detector
(B)
Ethyl alcohol is used as a quenching gas
(C)
The electric field strength decreases from the axis to the edge of the tube and the direction of the field is radially outward
(D)
The electric field increases from the axis to the edge of the tube and the field direction is radially inward
Check Answer
Option A, B, C
Q.No:21 GATE-2024
Consider the induced nuclear fission reaction
\[
^{235}_{92}U + n \rightarrow \, ^{93}_{37}Rb + \, ^{141}_{55}Cs + 2n
\]
where neutron momenta in both initial and final states are negligible. The ratio of the kinetic energies (KE) of the daughter nuclei,
\[
\frac{KE(^{93}_{37}Rb)}{KE(^{141}_{55}Cs)}
\]
is ____________
(A) \(\frac{93}{141}\)
(B) \(\frac{141}{93}\)
(C) \(1\)
(D) \(0\)
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:22 GATE-2024
Binding energy and rest mass energy of a two-nucleon bound state are denoted by \( B \) and \( mc^2 \), respectively, where \( c \) is the speed of light. The minimum energy of a photon required to dissociate the bound state is
(A) \( B \)
(B) \( B \left( 1 + \frac{B}{2mc^2} \right) \)
(C) \( B \left( 1 - \frac{B}{2mc^2} \right) \)
(D) \( B - mc^2 \)
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:23 GATE-2024
Let \( N_e \) and \( T_e \), respectively, denote number and kinetic energy of electrons produced in a nuclear beta decay. Which one of the following distributions is correct?
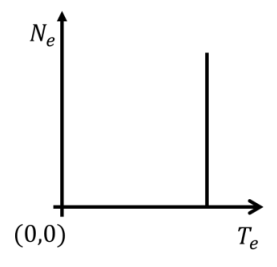
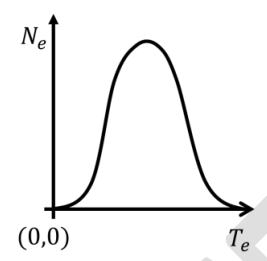
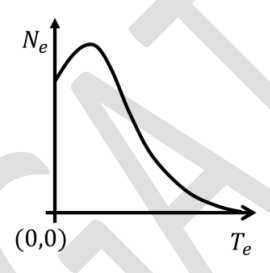
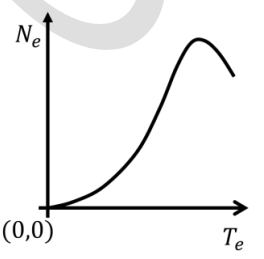
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:24 GATE-2025
Nuclear radiation emitted from a \(^{60}\mathrm{Co}\) radioactive source is detected by a
photomultiplier tube (PMT) coupled to a scintillator crystal.
Which of the following option(s) is/are correct?
A) \(\gamma\) radiation from \(^{60}\mathrm{Co}\) will directly hit the photocathode of the PMT
without interacting with the scintillator crystal and produce a signal
B) \(\beta\) radiation from \(^{60}\mathrm{Co}\) source interacts with the scintillator crystal,
producing \(\gamma\) radiation, which will hit the photocathode of the PMT and produce a signal
C) A mu-metal shield is put all around the PMT to nullify the effect of external electric fields
D) A mu-metal shield is put all around the PMT to nullify the effect of external magnetic fields
Check Answer
Option B,D
Q.No:25 GATE-2025
Two projectile protons \(P_{1}\) and \(P_{2}\), both with spin up (along the \(+z\) direction), are scattered from another fixed target proton \(T\) with spin up at rest in the \(xy\) plane, as shown in the figure. They scatter one at a time. The nuclear interaction potential between both the projectiles and the target proton is \(\lambda\,\vec{L}\cdot\vec{S}\), where \(\vec{L}\) is the orbital angular momentum of the system with respect to the target, \(\vec{S}\) is the spin angular momentum of the system and \(\lambda\) is a negative constant in appropriate units. Which one of the following is correct?
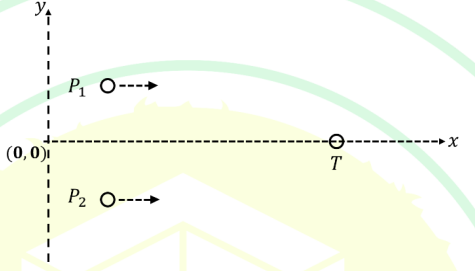
A) \(P_{1}\) will be scattered in the \(+y\) direction (upward) and \(P_{2}\) will be scattered in the \(-y\) direction (downward)
B) \(P_{1}\) will be scattered in the \(+y\) direction (upward) and \(P_{2}\) will be scattered in the \(+y\) direction (upward)
C) \(P_{1}\) will be scattered in the \(-y\) direction (downward) and \(P_{2}\) will be scattered in the \(+y\) direction (upward)
D) \(P_{1}\) will be scattered in the \(-y\) direction (downward) and \(P_{2}\) will be scattered in the \(-y\) direction (downward)
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:26 GATE-2025
Consider two hypothetical nuclei \(X_{1}\) and \(X_{2}\) undergoing \(\beta\) decay, resulting in nuclei \(Y_{1}\) and \(Y_{2}\), respectively. The decay scheme and the corresponding \(J^{P}\) values of the nuclei are given in the figure. Which of the following option(s) is/are correct? \((J\) is the total angular momentum and \(P\) is parity)
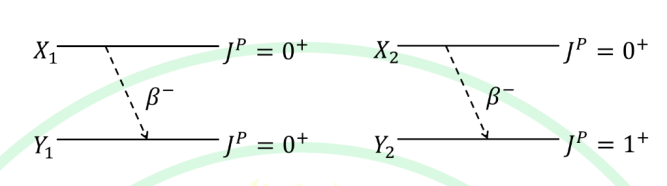
A) \(X_{1}\to Y_{1}\) is Fermi transition and \(X_{2}\to Y_{2}\) is Fermi transition
B) \(X_{1}\to Y_{1}\) is Fermi transition and \(X_{2}\to Y_{2}\) is Gamow–Teller transition
C) \(X_{1}\to Y_{1}\) is Gamow–Teller transition and \(X_{2}\to Y_{2}\) is Fermi transition
D) \(X_{1}\to Y_{1}\) is Gamow–Teller transition and \(X_{2}\to Y_{2}\) is Gamow–Teller transition
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:1 CSIR Dec-2014
In deep inelastic scattering electrons are scattered off protons to determine if a proton has any internal structure. The energy of the electron for this must be at least
(1)
\(1.25\times 10^9 eV\)
(2)
\(1.25\times 10^{12} eV\)
(3)
\(1.25\times 10^6 eV\)
(4)
\(1.25\times 10^8 eV\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:2 CSIR Dec-2015
A positron is suddenly absorbed by the nucleus of a tritium \(({^{3}_{1}H})\) atom to turn the latter into a \({He+}\) ion. If the electron in the tritium atom was initially in the ground state, the probability that the resulting \({He+}\) ion will be in its ground state is
(1)
\(1\)
(2)
\(\frac{8}{9}\)
(3)
\(\frac{128}{243}\)
(4)
\(\frac{512}{729}\)
Check Answer
Option 4
Q.No:3 CSIR June-2016
In the large hadron collider (LHC), two equal energy proton beams traverse in opposite directions along a circular path of length \(27 km\). If the total centre of mass energy of a proton-proton pair is \(14 TeV\), which of the following is the best approximation for the proper time taken by a proton to traverse the entire path?
(1)
\(12 ns\)
(2)
\(12 \mu s\)
(3)
\(1.2 ns\)
(4)
\(0.12 \mu s\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:4 CSIR Dec-2016
What should be the minimum energy of a photon for it to split an \(\alpha\)-particle at rest into a tritium and a proton? (The masses of \({^{4}_{2} He}\), \({^{3}_{1} H}\) and \({^{1}_{1} H}\) are \(4.0026 amu, 3.0161 amu\) and \(1.0073 amu\), respectively, and \(1 amu \approx 938 MeV\).)
(1)
\(32.2 MeV\)
(2)
\(3 MeV\)
(3)
\(19.3 MeV\)
(4)
\(931.5 MeV\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:5 CSIR June-2017
If in a spontaneous \(\alpha\)-decay of \({^{232}_{92}U}\) at rest, the total energy released in the reaction is \(Q\), then the energy carried by the \(\alpha\)-particle is
(1)
\(57Q/58\)
(2)
\(Q/57\)
(3)
\(Q/58\)
(4)
\(23Q/58\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:6 CSIR June-2017
The range of the nuclear force between two nucleons due to the exchange of pions is \(1.40 fm\). If the mass of the pion is \(140 MeV/c^2\) and the mass of the rho-meson is \(770 MeV/c^2\), then the range of the force due to exchange of rho-mesons is
(1)
\(1.40 fm\)
(2)
\(7.70 fm\)
(3)
\(0.25 fm\)
(4)
\(0.18 fm\)
Check Answer
Option 3
Q.No:7 CSIR Dec-2017
The first excited state of the rotational spectrum of the nucleus \({^{238}_{92}U}\) has an energy \(45 keV\) above the ground state. The energy of the second excited state (in keV) is
(1)
\(150\)
(2)
\(120\)
(3)
\(90\)
(4)
\(60\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:8 CSIR June-2018
The reaction \({^{63} Cu_{29}}+p\to {^{63} Zn_{30}}+n\) is followed by a prompt \(\beta\)-decay of zinc \({^{63} Zn_{30}}\to {^{63} Cu_{29}}+e^{+}+\nu_{e}\). If the maximum energy of the positron is \(2.4 MeV\), the \(Q\)-value of the original reaction in MeV is nearest to [Take the masses of electron, proton and neutron to be \(0.5 MeV/c^2, 938 MeV/c^2\) and \(939.5 MeV/c^2\), respectively.]
(1)
\(-4.4\)
(2)
\(-2.4\)
(3)
\(-4.8\)
(4)
\(-3.4\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:9 CSIR Dec-2018
A nucleus decays by the emission of a gamma ray from an excited state of spin-parity \(2^{+}\) to the ground state with spin-parity \(0^{+}\). What is the type of the corresponding radiation?
(1)
magnetic dipole
(2)
electric quadrupole
(3)
electric dipole
(4)
magnetic quadrupole
Check Answer
Option 2
Q.No:10 CSIR Dec-2018
The low lying energy levels due to the vibrational excitations of an even-even nucleus are shown in the figure below.

The spin-parity \(j^p\) of the level \(E_1\) is
(1)
\(1^{+}\)
(2)
\(1^{-}\)
(3)
\(2^{-}\)
(4)
\(2^{+}\)
Check Answer
Option 4
Q.No:11 CSIR June-2019
An excited state of a \({^{8}_{4} Be}\) nucleus decays into two \(\alpha\)-particles which are in a spin-parity \(0^{+}\) state. If the mean life-time of this decay is \(10^{-22} s\), the spin-parity of the excited state of the nucleus is
(1)
\(2^{+}\)
(2)
\(3^{+}\)
(3)
\(0^{-}\)
(4)
\(4^{-}\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:12 Assam CSIR Dec-2019
A beam of protons on a \ce{Li} target produces two \(\alpha\)-particles through the reaction \(p+{^{7}_{3} Li}\to 2 {^{4}_{2} He}\). The atomic masses of \({^{7} Li}, {^{4} He}\) and \({^{1} H}\) are \(7.0160 u, 4.0026 u\) and \(1.0078 u\), respectively, where \(1 u\) is \(930 MeV/c^2\). The \(Q\)-value of the reaction is closest to
(1)
\(15.2 MeV/c^2\)
(2)
\(16.0 MeV/c^2\)
(3)
\(18.6 MeV/c^2\)
(4)
\(17.3 MeV/c^2\)
Check Answer
Option 4
Q.No:13 CSIR Feb-2022
The nuclei of \(^{137}C_S\) decay by the emission of \(\beta\)-particles with a half-life of \(30.08\) years.
The activity (in units of disintegrations per second or Bq ) of a 1mg source of \(^{137}C_S\), prepared on
January \(1, 1980\) , as measured on January \(1, 2021\) is closest to
(1)
\(1.79\times10^{16}\)
(2)
\(1.79\times10^{9}\)
(3)
\(1.24\times10^{16}\)
(4)
\(1.24\times10^{9}\)
Check Answer
Option 4
Q.No:14 CSIR Feb-2022
A \(^{60}Co\) nucleus \(\beta\) -decays from its ground state with \(J^P=5^+\)to a state of \(^{60}Ni\) with \(J^P=4^+\) . From the angular momentum selection rules, the allowed values of the orbital angular
momentum \(L\) and the total spin \(S\) of the electron-antineutrino pair are
(1)
\(L=0\) and \(S=1\)
(2)
\(L=1\) and \(S=0\)
(3)
\(L=0\) and \(S=0\)
(4)
\(L=1\) and \(S=1\)
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:15 CSIR Feb-2022
The \(Q\)-value of the \(\alpha\) -decay of \(\hspace{2mm}\) \(^{232}Th\) to the ground state of \(\hspace{2mm}\)\(^{228}Ra\) in \(4082\) keV . The
maximum possible kinetic energy of the \(\alpha\)-particle is closest to
(1)
\(4082\)\(\hspace{1mm}\)keV
(2)
\(4050\)\(\hspace{1mm}\)keV
(3)
\(4035\)\(\hspace{1mm}\)keV
(4)
\(4012\)\(\hspace{1mm}\)keV
Check Answer
Option 4
Q.No:16 CSIR Sep-2022
The tensor component of the nuclear force may be inferred from the fact that deuteron nucleus \(^2H_1\)
(1)
has only one bound state with total spin S=1
(2)
has non zero electric quadrupole moment in its ground state
(3)
is stable while triton \(^3H_1\) is unstable
(4)
is the only two nucleon bound state
Check Answer
Option 2
Q.No:17 CSIR Sep-2022
Thermal neutrons may be detected most efficiently by a
(1)
\(^6Li\) loaded plastic scintillator
(2)
Geiger-Müller counter
(3)
inorganic scintillator \(CaF_2\)
(4)
silicon detector
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:18 CSIR June-2023
The nucleus of \(^{40}K\) (of spin-parity \(4^+\) in the ground state) is unstable and decays to \(^{40}Ar\). The mass difference between these two nuclei is \(\Delta Mc^2=1504.4 \hspace{1mm}keV\). The nucleus \(^{40}Ar\) has an excited state at \(1460.8 \hspace{1mm}keV\) with spin-parity \(2^+\). The most probable decay mode of \(^{40}K\) is by
1) a \(\beta^+\)-decay to the \(2^+\) state of \(^{40}Ar\)
2) an electron capture to the \(2^+\) state of \(^{40}Ar\)
3) an electron capture to the ground state of \(^{40}Ar\)
4) a \(\beta^+\)-decay to the ground state of \(^{40}Ar\)
Check Answer
Option 2
Q.No:19 CSIR June-2023
The energy (in keV) and spin-parity values \(E(J^p)\) of the low lying excited states of a nucleus of mass number \(A=152\), are \(122(2^+)\), \(366(4^+)\), \(707(6^+)\), and \(1125(8^+)\). It may be inferred that these energy levels correspond to a
1) rotational spectrum of a deformed nucleus
2) rotational spectrum of a spherically symmetric nucleus
3) vibrational spectrum of a deformed nucleus
4) vibrational spectrum of a spherical symmetric nucleus
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:20 CSIR Dec-2023
The ground state of \( ^{207}_{82}\text{Pb} \) nucleus has spin-parity \( j^{\pi} = \left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{-} \), while the first excited state has \( j^{\pi} = \left(\frac{5}{2}\right)^{-} \). For the transition from the first excited state to the ground state, possible multipolarities of emitted electromagnetic radiation are
1) E2, E3
2) M2, M3
3) M2, E3
4) E2, M3
Check Answer
Option 4
Q.No:21 CSIR June-2024
In a scattering experiment, a beam of \( e^- \) with an energy of 420 MeV scatters off an atomic nucleus. If the first minimum of the differential cross section is observed at a scattering angle of 45°, the radius of the nucleus (in fermi) is closest to
1) 0.4
2) 8.0
3) 2.5
4) 0.8
Check Answer
Option 3
Q.No:22 CSIR Dec-2024
The masses of proton, neutron, Polonium and Lead nuclei are as follows:
\(m_{p} = 1.007825\ \text{a.u.},\quad m_{n} = 1.008665\ \text{a.u.}\)
\(m(^{210}_{84}\mathrm{Po}) = 209.982876\ \text{a.u.},\quad m(^{206}_{82}\mathrm{Pb}) = 205.974455\ \text{a.u.}\)
Binding energy of \(^{4}_{2}\mathrm{He}\) is \(28.80\ \mathrm{MeV}\) and \(1\ \text{a.u.} = 931.99\ \mathrm{MeV}/c^{2}\).
The binding energies of \(^{210}_{84}\mathrm{Po}\), \(^{206}_{82}\mathrm{Pb}\) and the \(Q\) value of the \(\alpha\)-decay of \(^{210}_{84}\mathrm{Po}\) are closest to
1) 1645.21 MeV,1622.33 MeV, 5.92 MeV
2) 1645.21 MeV, 1622.33 MeV, -5.92 MeV
3) 1545.21 MeV, 1522.33 MeV, -5.92 MeV
4) 1645.21 MeV, 1522.33 MeV, 5.92 MeV
Check Answer
Option 1
Q.No:23 CSIR Dec-2024
Naturally occurring uranium is a mixture of the \(^{238}\mathrm{U}\) (99.28%) and \(^{235}\mathrm{U}\) (0.72%) isotopes. The life times are \(\tau(^{235}\mathrm{U}) = 1\times 10^{9}\) years and \(\tau(^{238}\mathrm{U}) = 6.6\times 10^{9}\) years. What is the closest value of the age of the solar system if one assumes that at its creation both isotopes were present in equal quantities?
1) \(6.2\times 10^{9}\) years
2) \(5.8\times 10^{9}\) years
3) \(4.7\times 10^{9}\) years
4) \(7.2\times 10^{9}\) years
Check Answer
Option 2
Q.No:24 CSIR June-2025
If the binding energies per nucleon of the nuclei \(X(A = 240)\) and \(Y(A = 120)\) are \(7.6\ \text{MeV}\) and \(8.5\ \text{MeV}\) respectively, the energy released in the symmetric fission \(X \rightarrow Y + Y\) is
1) \(94\ \text{MeV}\)
2) \(9.4\ \text{MeV}\)
3) \(108\ \text{MeV}\)
4) \(216\ \text{MeV}\)
