Q.No:1 GATE-2012
For an ideal Fermi gas in three dimensions, the electron velocity \(v_F\) at the Fermi surface is related to electron concentration \(n\) as,
(A)
\(v_F\propto n^{2/3}\)
(B)
\(v_F\propto n\)
(C)
\(v_F\propto n^{1/2}\)
(D)
\(v_F\propto n^{1/3}\)
Check Answer
Option D
Q.No:2 GATE-2012
The total energy, \(E\) of an ideal non-relativistic Fermi gas in three dimensions is given by \(E\propto \frac{N^{5/3}}{V^{2/3}}\) where \(N\) is the number of particles and \(V\) is the volume of the gas. Identify the CORRECT equation of state (\(P\) being the pressure),
(A)
\(PV=\frac{1}{3}E\)
(B)
\(PV=\frac{2}{3}E\)
(C)
\(PV=E\)
(D)
\(PV=\frac{5}{3}E\)
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:3 GATE-2012
Which one of the following CANNOT be explained by considering a harmonic approximation for the lattice vibrations in solids?
(A)
Debye's \(T^3\) law
(B)
Dulong Petit's law
(C)
Optical branches in lattices
(D)
Thermal expansion
Check Answer
Option D
Q.No:4 GATE-2013
If Planck's constant were zero, then the total energy contained in a box filled with radiation of all frequencies at temperature \(T\) would be (\(k\) is the Boltzmann constant and \(T\) is nonzero)
(A)
Zero
(B)
Infinite
(C)
\(\frac{3}{2}kT\)
(D)
\(kT\)
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:5 GATE-2013
The number of distinct ways of placing four indistinguishable balls into five distinguishable boxes is ____________.
Check Answer
Ans 70
Q.No:6 GATE-2014
Which one of the following is a fermion?
(A)
\(\alpha\) particle
(B)
\({_{4} Be^{7}}\) nucleus
(C)
Hydrogen atom
(D)
Deuteron
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:7 GATE-2014
For a free electron gas in two dimensions, the variation of the density of states, \(N(E)\) as a function of energy \(E\), is best represented by

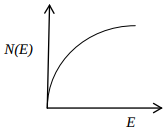
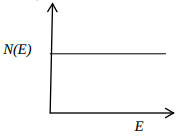

Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:8 GATE-2014
Consider a system of \(3\) fermions, which can occupy any of the \(4\) available energy states with equal probability. The entropy of the system is
(A)
\(k_B \ln{2}\)
(B)
\(2k_B \ln{2}\)
(C)
\(2k_B \ln{4}\)
(D)
\(3k_B \ln{4}\)
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:9 GATE-2015
In Bose-Einstein condensates, the particles
(A)
have strong interparticle attraction
(B)
condense in real space
(C)
have overlapping wavefunctions
(D)
have large and positive chemical potential
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:10 GATE-2015
For a black body radiation in a cavity, photons are created and annihilated freely as a result of emission and absorption by the walls of the cavity. This is because
(A)
the chemical potential of the photons is zero
(B)
photons obey Pauli exclusion principle
(C)
photons are spin-\(1\) particles
(D)
the entropy of the photons is very large
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:11 GATE-2015
The energy dependence of the density of states for a two dimensional non-relativistic electron gas is given by, \(g(E)=CE^n\), where \(C\) is constant. The value of \(n\) is ___________.
Check Answer
Ans 0
Q.No:12 GATE-2015
Given that the Fermi energy of gold is \(5.54 eV\), the number density of electrons is __________ \(times 10^{28} m^{-3}\) (upto one decimal place)
(\(\text{Mass of electron}=9.11\times 10^{-31} kg; h=6.626\times 10^{-34} J.s\);
\(1 eV=1.6\times 10^{-19} J\))
Check Answer
Ans 5.9-6.0
Q.No:13 GATE-2016
Consider a metal which obeys the Sommerfeld model exactly. If \(E_F\) is the Fermi energy of the metal at \(T=0 K\) and \(R_H\) is its Hall coefficient, which of the following statements is correct?
(A)
\(R_H\propto E_F^{3/2}\)
(B)
\(R_H\propto E_F^{2/3}\)
(C)
\(R_H\propto E_F^{-3/2}\)
(D)
\(R_H\) is independent of \(E_F\)
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:14 GATE-2016
Consider a system having three energy levels with energies \(0, 2\varepsilon\) and \(3\varepsilon\), with respective degeneracies of \(2, 2\) and \(3\). Four bosons of spin zero have to be accommodated in these levels such that the total energy of the system is \(10\varepsilon\). The number of ways in which it can be done is ____________.
Check Answer
Ans 18
Q.No:15 GATE-2016
The Fermi energies of two metals \(X\) and \(Y\) are \(5 eV\) and \(7 eV\) and their Debye temperatures are \(170 K\) and \(340 K\), respectively. The molar specific heats of these metals at constant volume at low temperatures can be written as \((C_V)_X=\gamma_X T+A_X T^3\) and \((C_V)_Y=\gamma_Y T+A_Y T^3\), where \(\gamma\) and \(A\) are constants. Assuming that the thermal effective mass of the electrons in the two metals are same, which of the following is correct?
(A)
\(\frac{\gamma_X}{\gamma_Y}=\frac{7}{5}, \frac{A_X}{A_Y}=8\)
(B)
\(\frac{\gamma_X}{\gamma_Y}=\frac{7}{5}, \frac{A_X}{A_Y}=\frac{1}{8}\)
(C)
\(\frac{\gamma_X}{\gamma_Y}=\frac{5}{7}, \frac{A_X}{A_Y}=\frac{1}{8}\)
(D)
\(\frac{\gamma_X}{\gamma_Y}=\frac{5}{7}, \frac{A_X}{A_Y}=8\)
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:16 GATE-2017
Consider a \(2\)-dimensional electron gas with a density of \(10^{19} m^{-2}\). The Fermi energy of the system is __________ eV (up to two decimal places).
Check Answer
Ans 2.32-2.40
Q.No:17 GATE-2017
The energy density and pressure of a photon gas are given by \(u=aT^4\) and \(P=u/3\), where \(T\) is the temperature and \(a\) is the radiation constant. The entropy per unit volume is given by \(\alpha aT^3\). The value of \(\alpha\) is __________. (up to two decimal places).
Check Answer
Ans 1.30-1.36
Q.No:18 GATE-2017
Consider two particles and two non-degenerate quantum levels 1 and 2. Level 1 always contains a particle. Hence, what is the probability that level 2 also contains a particle for each of the two cases:
(i) when the two particles are distinguishable and
(ii) when the two particles are bosons?
(A)
(i) \(1/2\) and (ii) \(1/3\)
(B)
(i) \(1/2\) and (ii) \(1/2\)
(C)
(i) \(2/3\) and (ii) \(1/2\)
(D)
(i) \(1\) and (ii) \(0\)
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:19 GATE-2018
At low temperatures (\(T\)), the specific heat of common metals is described by (with \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) as constants)
(A)
\(\alpha T+\beta T^3\)
(B)
\(\beta T^3\)
(C)
\(\exp{(-\alpha/T)}\)
(D)
\(\alpha T+\beta T^5\)
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:20 GATE-2018
If \(X\) is the dimensionality of a free electron gas, the energy (\(E\)) dependence of density of states is given by \(E^{\frac{1}{2}X-Y}\), where \(Y\) is __________________.
Check Answer
Ans 1
Q.No:21 GATE-2018
Three particles are to be distributed in four non-degenerate energy levels. The possible number of ways of distribution:
(i) for distinguishable particles, and
(ii) for identical Bosons, respectively, is
(A)
(i) 24, (ii) 4
(B)
(i) 24, (ii) 20
(C)
(i) 64, (ii) 20
(D)
(i) 64, (ii) 16
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:22 GATE-2019
A large number \(N\) of ideal bosons, each of mass \(m\), are trapped in a three-dimensional potential \(V(r)=\frac{m\omega^2 r^2}{2}\). The bosonic system is kept at temperature \(T\) which is much lower than the Bose-Einstein condensation temperature \(T_c\). The chemical potential (\(\mu\)) satisfies
(A)
\(\mu\leq \frac{3}{2}\hbar \omega\)
(B)
\(2\hbar \omega>\mu>\frac{3}{2}\hbar \omega\)
(C)
\(3\hbar \omega>\mu>2\hbar \omega\)
(D)
\(\mu=3\hbar \omega\)
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:23 GATE-2019
The energy-wavevector (\(E\)-\(k\)) dispersion relation for a particle in two dimensions is \(E=Ck\), where \(C\) is a constant. If its density of states \(D(E)\) is proportional to \(E^p\) then the value of \(p\) is _____________.
Check Answer
Ans 1
Q.No:24 GATE-2019
At temperature \(T\) Kelvin (K), the value of the Fermi function at an energy \(0.5 eV\) above the Fermi energy is \(0.01\). Then \(T\), to the nearest integer, is ___________ (\(k_B=8.62\times 10^{-5} eV/K\))
Check Answer
Ans 1260-1266
Q.No:25 GATE-2020
Choose the correct statement related to the Fermi energy (\(E_F\)) and the chemical potential (\(\mu\)) of a metal
(A)
\(\mu=E_F\) only at \(0 K\)
(B)
\(\mu=E_F\) at finite temperature
(C)
\(\mu<E_F\) at \(0 K\)
(D)
\(\mu<E_F\) at \(0 K\)
Check Answer
Option A
Q.No:26 GATE-2021
For a finite system of Fermions where the density of states increases with energy, the chemical potential
(A)
decreases with temperature
(B)
increases with temperature
(C)
does not vary with temperature
(D)
corresponds to the energy where the occupation probability is \(0.5\)
Check Answer
Option A & D
Q.No:27 GATE-2021
A system of two atoms can be in three quantum states having energies \(0, \epsilon\) and \(2\epsilon\). The system is in equilibrium at temperature \(T=(k_B \beta)^{-1}\). Match the following \({\bf Statistics}\) with the \({\bf Partition function}\).

(A)
\({\bf CD}:{\bf Z1}, {\bf CI}:{\bf Z2}, {\bf FD}:{\bf Z3}, {\bf BE}:{\bf Z4}\)
(B)
\({\bf CD}:{\bf Z2}, {\bf CI}:{\bf Z3}, {\bf FD}:{\bf Z4}, {\bf BE}:{\bf Z1}\)
(C)
\({\bf CD}:{\bf Z3}, {\bf CI}:{\bf Z4}, {\bf FD}:{\bf Z1}, {\bf BE}:{\bf Z2}\)
(D)
\({\bf CD}:{\bf Z4}, {\bf CI}:{\bf Z1}, {\bf FD}:{\bf Z2}, {\bf BE}:{\bf Z3}\)
Check Answer
Option C
Q.No:28 GATE-2022
In a two-dimensional square lattice, frequency \(\omega\) of phonons in the long wavelength limit changes linearly with the wave vector \(k\). Then the density of states of phonons is proportional to
(a)
\(\omega\)
(b)
\(\omega^2\)
(c)
\(\sqrt{\omega}\)
(d)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{\omega}}\)
Check Answer
Option a
Q.No:29 GATE-2023
For a non-magnetic metal, which one of the following graphs best represents the behaviour of \(\frac{C}{T}\) vs. \(T^2\), where \(C\) is the heat capacity and \(T\) is the temperature?
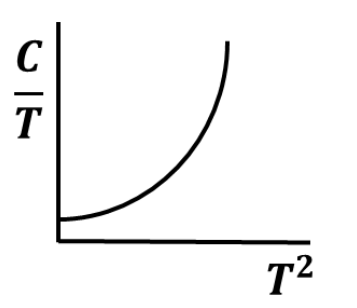
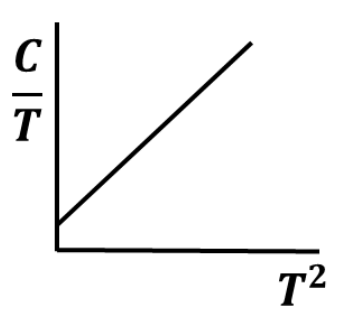
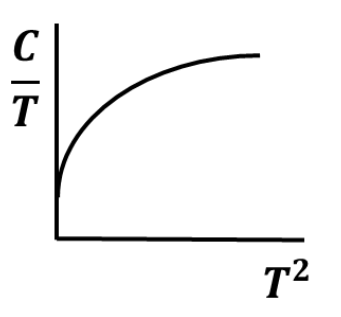
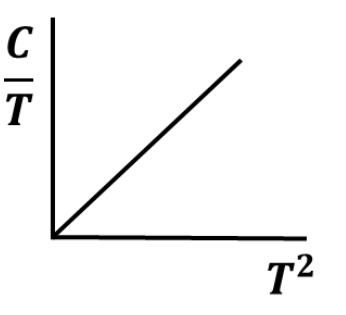
Check Answer
Option B
Q.No:30 GATE-2023
Two identical, non-interacting \(^4 He _2\) atoms are distributed among 4 different nondegenerate energy levels. The probability that they occupy different energy levels is \(p\). Similarly, two \(^3 He_2\) atoms are distributed among 4 different non-degenerate energy levels, and the probability that they occupy different levels is \(q\). What is
the value of \(\frac{p}{q}\) (rounded off to one decimal place)?
Check Answer
Ans 0.6
Q.No: 31 GATE-2024
Consider a three-dimensional system of non-interacting bosons with zero chemical potential. The energy of the system \( \varepsilon \propto k^2 \), where \( k \) is the wavevector. The low temperature specific heat of the system at constant volume depends on the temperature as \( C_v \propto T^{\frac{n}{2}} \). The value of \( n \) is _____ (in integer).
Check Answer
Ans 3
Q.No: 32 GATE-2024
The canonical partition function of an ideal gas is
\[
Q(T,V,N) = \frac{1}{N!} \left[ \frac{V}{(\lambda(T))^3} \right]^N
\]
where \( T \), \( V \), \( N \), and \( \lambda(T) \) denote temperature, volume, number of particles, and thermal de Broglie wavelength, respectively. Let \( k_B \) be the Boltzmann constant and \( \mu \) be the chemical potential. Take \( \ln(N!) = N\ln(N) - N \).
If the number density \( \left( \frac{N}{V} \right) \) is \( 2.5 \times 10^{25} \, \text{m}^{-3} \) at a temperature \( T \), then the value of
\[
\frac{e^{\mu/(k_B T)}}{(\lambda(T))^3} \times 10^{-25}
\]
is ______ \(m^{-3}\) (rounded off to one decimal place).
Check Answer
Ans 2.5
Q.No: 33 GATE-2024
Crystal structures of two metals A and B are two-dimensional square lattices with the same lattice constant \( a \). Electrons in metals behave as free electrons. The Fermi surfaces corresponding to A and B are shown by solid circles in figures.
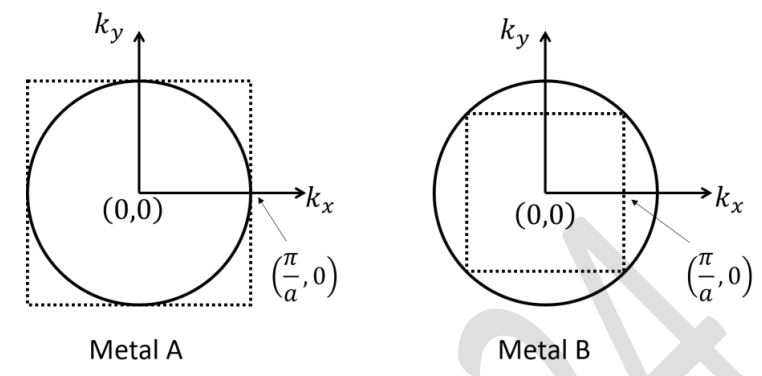
The electron concentrations in A and B are \( n_A \) and \( n_B \), respectively. The value of \( \frac{n_B}{n_A} \) is
(A) \( 3 \)
(B) \( 2 \)
(C) \( 3\sqrt{3} \)
(D) \( \sqrt{2} \)
Check Answer
option B
Q.No: 34 GATE-2025
Consider one mole of a monovalent metal at absolute zero temperature, obeying the
free electron model. Its Fermi energy is \(E_F\). The energy corresponding to the
filling of \(\frac{N_A}{2}\) electrons, where \(N_A\) is the Avogadro number, is
\(2^{\,n} E_F\). The value of \(n\) is
A) \(-\frac{2}{3}\)
B) \(+\frac{2}{3}\)
C) \(-\frac{1}{3}\)
D) \(-1\)
Check Answer
option A
Q.No: 35 GATE-2025
Consider a monatomic chain of length 30 cm. The phonon density of states is
\(1.2 \times 10^{-4} \, \text{s}\). Assuming the Debye model, the velocity of sound
in m/s (rounded off to one decimal place) is ______.
Check Answer
Ans 794 to 797
Q.No: 36 GATE-2025
A system of five identical, non-interacting particles with mass \(m\) and spin \( \frac{3}{2}\) is confined to a one-dimensional potential well of length \(L\). If the lowest energy of the system is
\[
N \frac{\pi^{2}\hbar^{2}}{2mL^{2}},
\]
the value of \(N\) (in integer) is ______..

Q.No.1 Discussion :
Ans
Q.No.2 Discussion :
Ans
Q.No.3 Discussion :
Q.No.4 Discussion :
My sol
Q.No.5 Discussion :
Solution
Q.No.6 Discussion :
Q No 6
Q.No.7 Discussion :
Ans
Q.No.8 Discussion :
Q.No.9 Discussion :
Q.No.10 Discussion :
Option A
Q.No.11 Discussion :
n=0
Q.No.12 Discussion :
Q.No.13 Discussion :
Q.No.14 Discussion :
solution
Q.No.15 Discussion :
solution
Q.No.16 Discussion :
Gate 2017
Q.No.17 Discussion :
Q No 17
Q.No.18 Discussion :
Q.No.19 Discussion :
Q19 Gate’18
Q19 Gate 2018
Q.No.20 Discussion :
Q20 GATE 2018
Q.No.21 Discussion :
Ans
Q.No.22 Discussion :
Q.No.23 Discussion :
ans
Q.No.24 Discussion :
Temperature is 1262K (approximate value)
Q.No.25 Discussion :
Q.No.26 Discussion :
Q.No.27 Discussion :
Ans
Q.No.28 Discussion :
Ans
Q.No.29 Discussion :
Ans
Q.No.30 Discussion :
Answer is 0.6
Q No 30